Brain Structure and Function
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF):
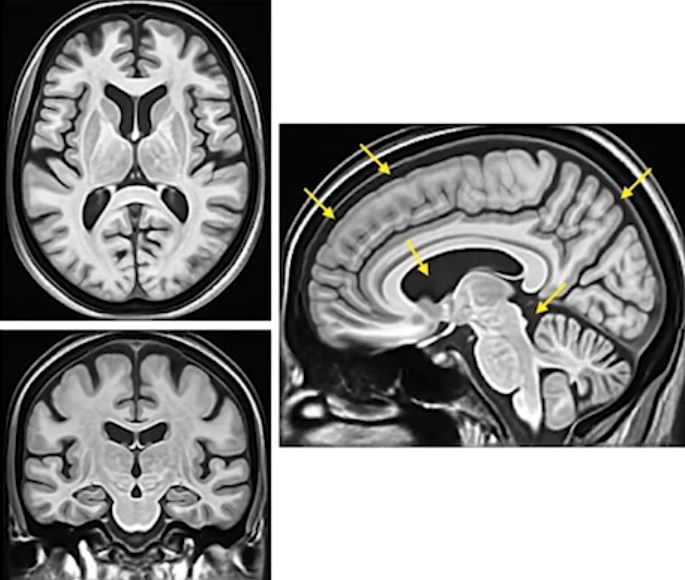
- Black part indicated by arrow
- Protects the brain from trauma by acting as a cushion.
- Provides nutrients to the brain.
- Helps remove waste products.
[!Explore More] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kaOphkMv2pM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9e9Lo0OPON4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D4gq8MILGns
Grey Matter:
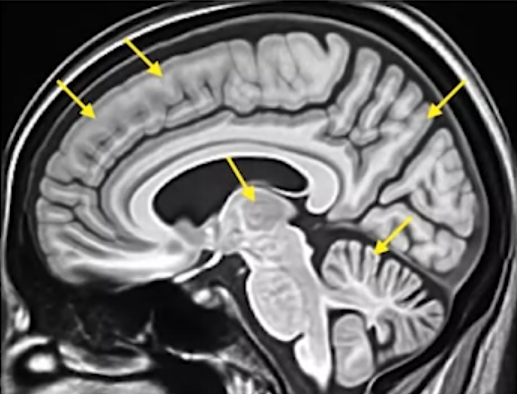
- Contains neuronal cell bodies responsible for information processing.
- Determines whether or not a signal is sent to the next cell.
White Matter:
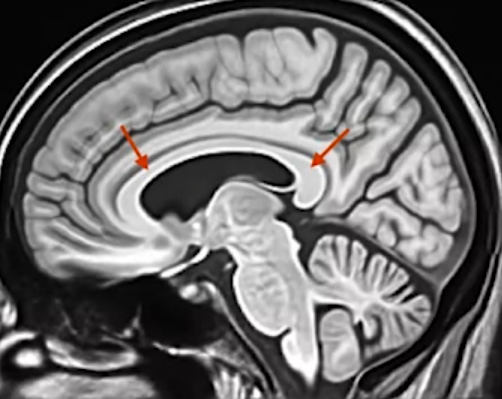
-
Consists of axon fibers that transmit information between brain regions.
-
Major bundles include:
- Anterior cingulate cortex (left-right hemisphere communication)
- Posterior cingulate cortex (left-right hemisphere communication)
- Corpus callosum (major left-right hemisphere communication bundle)
[!Explore More] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kR_jWUhmN2A https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZZQzMeFoZY0
Primary Motor Cortex:
- Located in the dorsal frontal lobe.
- Plans and executes movements.
- Cortical neurons send long axon down the spinal cord to initiate muscle movements.
- Orderly somatotopic organization:
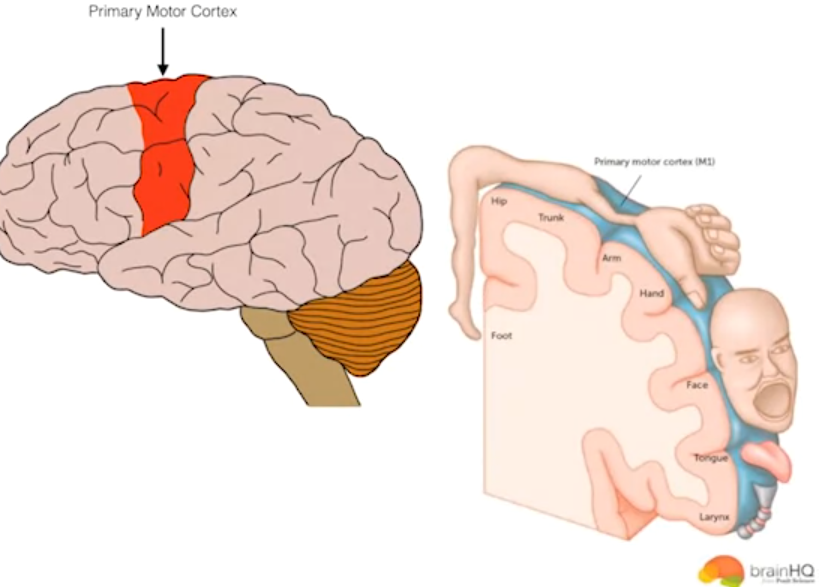
- Foot and leg area - medial and most middle
- Hand, face, tongue - more lateral
Primary Somatosensory Cortex:
- Receives sensory input from the entire body.
- Orderly somatotopic organization based on receptor density:
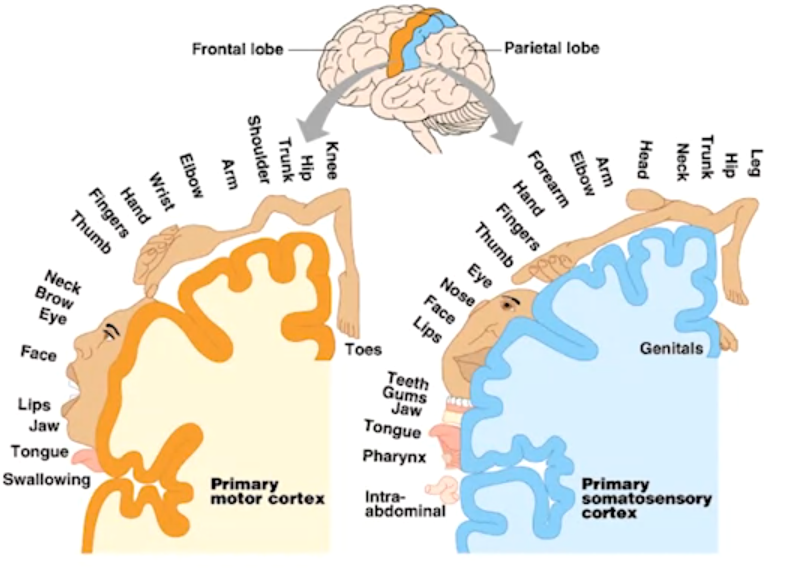
- Face, lips, eyes - larger cortical representation
- Shoulder, torso - smaller cortical representation
Thalamus:
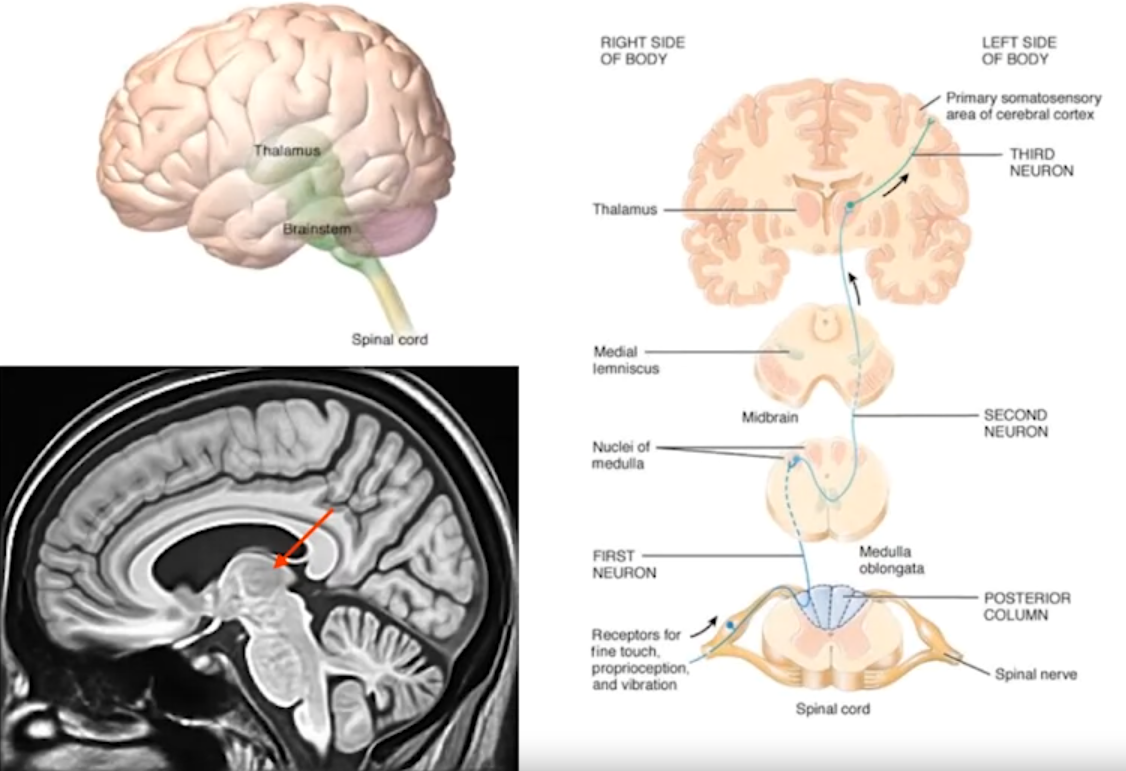
- Relays sensory and motor information throughout the brain.
- Regulates sleep and consciousness.
- Left thalamus receives sensory information from the right side of the body.
- Left motor cortex controls movement on the right side of the body (contralateral control).
Visual Cortex:
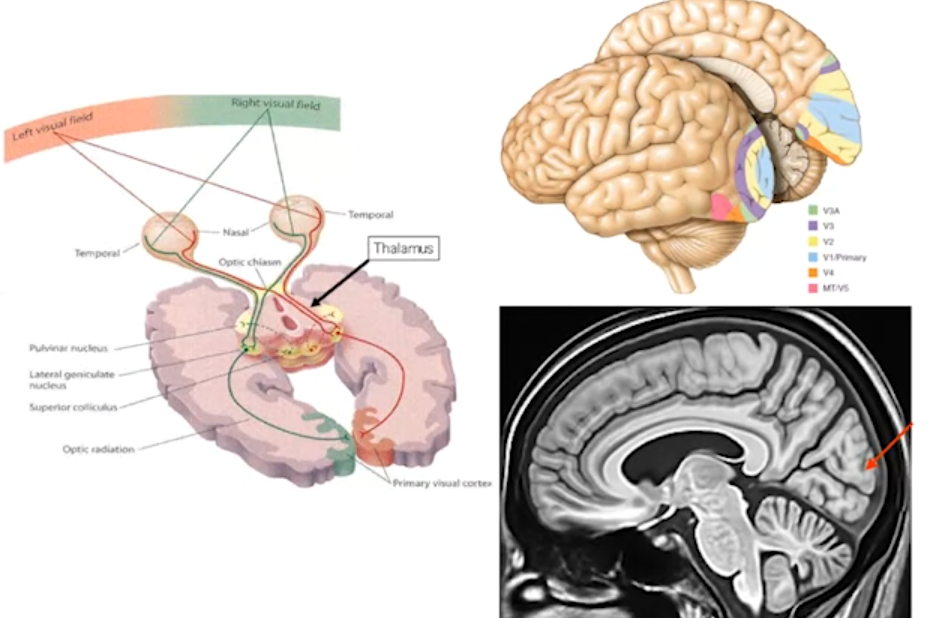
-
Processes visual features like orientation, motion, and color.
-
Organized by visual field:
- Right visual field processed by left hemisphere
- Left visual field processed by right hemisphere
-
Further subdivided for complex processing:
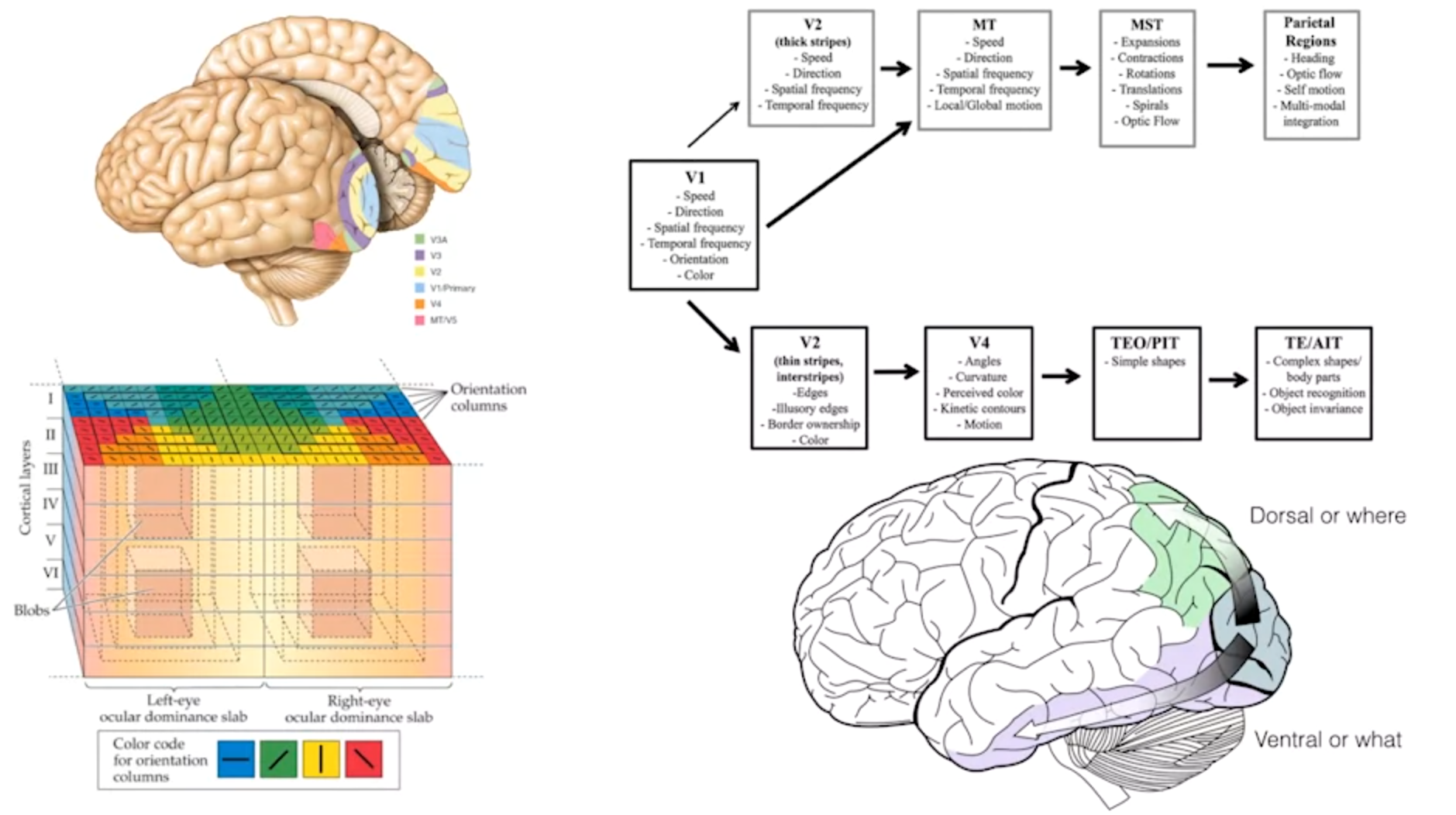
- V1: primary visual cortex (initial processing)
- Dorsal stream (V2, MT, MST, Parietal regions): processes where and how an object is moving
- Ventral stream (V2, V4, medial temporal lobe): processes what an object is
Cerebellum:
- Coordinates posture, balance, and movement smoothness.
- May also play a role in cognition (unclear).
Conclusion:
- The brain is composed of specialized regions with distinct functions.
- These regions work together to allow us to perceive and interact with the world.
- Next lecture: higher cognitive functions like language, memory, and attention.