This note covers the basic building blocks and organization of the human brain.
I. Cellular Composition
-
The brain consists of two main cell types:
-
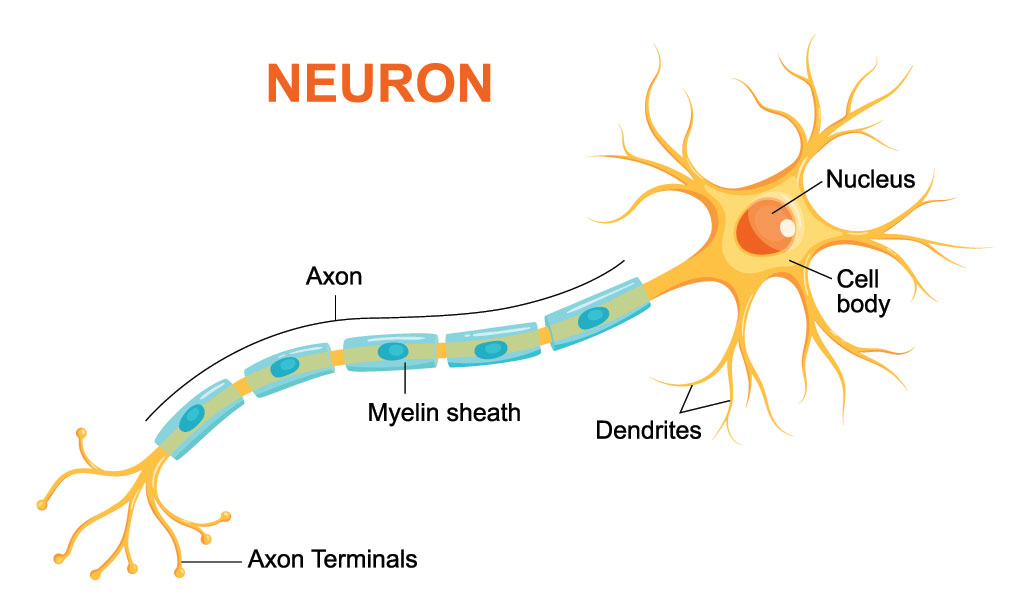
Neurons: Specialized cells for processing and transmitting information.
- They have various shapes and sizes depending on function.
- Key parts:
- Cell body: Contains nucleus and organelles for energy and protein synthesis.
- Dendrites: Receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon: Transmits signals to other neurons.
- Axon terminals: Communicate with other neurons.
-
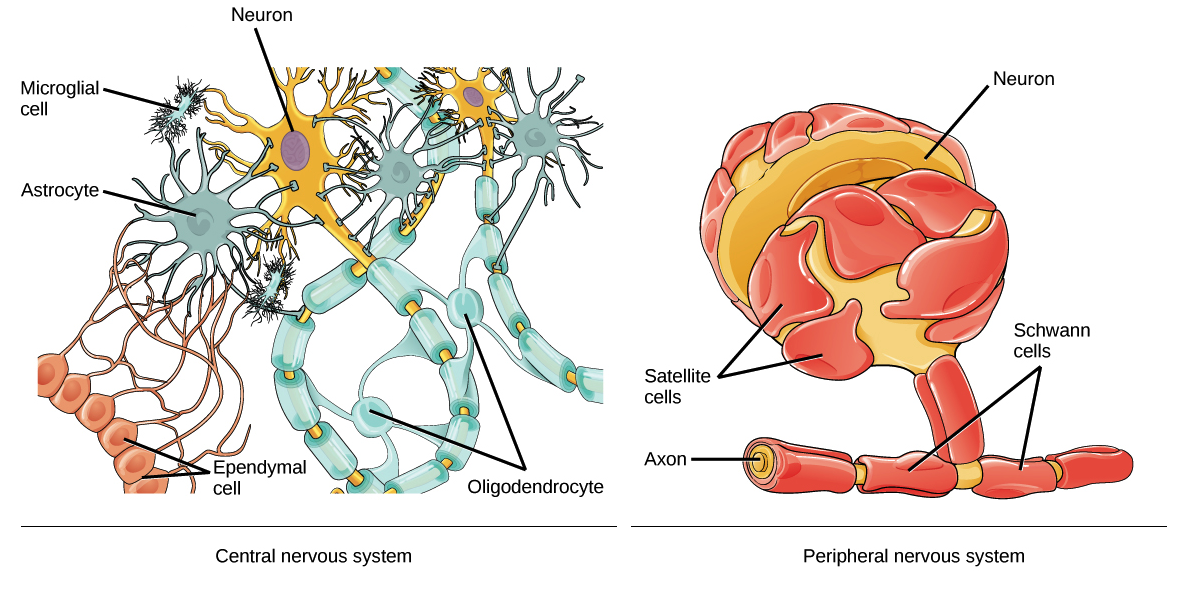
Glia: Supportive cells for neurons.
- Outnumber neurons and perform various functions:
- Provide structure and scaffolding.
- Maintain neuronal environment.
- Insulate axons (myelin) for faster signal transmission.
- Three type of Glia
- Astrocytes
- Microglia
- Oligodendrocytes
 II. Brain Organization
II. Brain Organization
- Outnumber neurons and perform various functions:
-
-
Large group of similar and spatially organized neurons form the basis of dissociable brain structure and networks
 There are three main ways to organize the brain:
There are three main ways to organize the brain: -
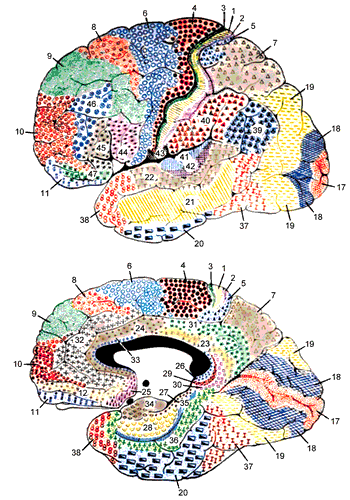
Cytoarchitectural Organization (Brodmann Areas):
- Based on cell structure and composition.
- Defined by Korbinian Brodmann in 1909.
- Still used to locate brain regions in neuroimaging.
- Applicable to various mammals (human, hedgehog, rabbit, etc.)
- Brain atlases provide detailed Brodmann area information. (Print & electronic)
[!Explore More] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brodmann_area https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/brodmann-areas
-
Functional Networks:
- Groups of brain structures connected for specific functions.
- Examples:
- Striatum (includes nucleus accumbens, caudate nucleus, putamen) - involved in reward and movement.
- Medial temporal lobe (hippocampus, entorhinal cortex, perirhinal cortex) - crucial for memory formation.
-
Lobes:
- Rudimentary anatomical classification based on location.
- Six lobes with generally associated functions:
- Frontal lobe: involved in planning, decision-making, movement.
- Parietal lobe: involved in processing touch, spatial awareness.
- Occipital lobe: involved in processing vision.
- Temporal lobe: involved in processing hearing, memory, emotion.
- Limbic lobe: involved in processing emotions and memory.
- Insular cortex: involved in various functions like taste, self-awareness.
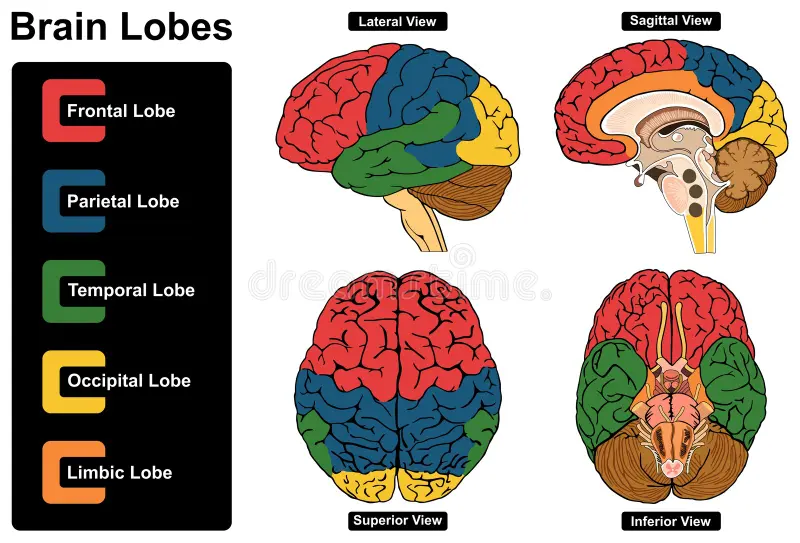
Understanding the brain’s cellular composition and organization is crucial for studying its function and dysfunction.
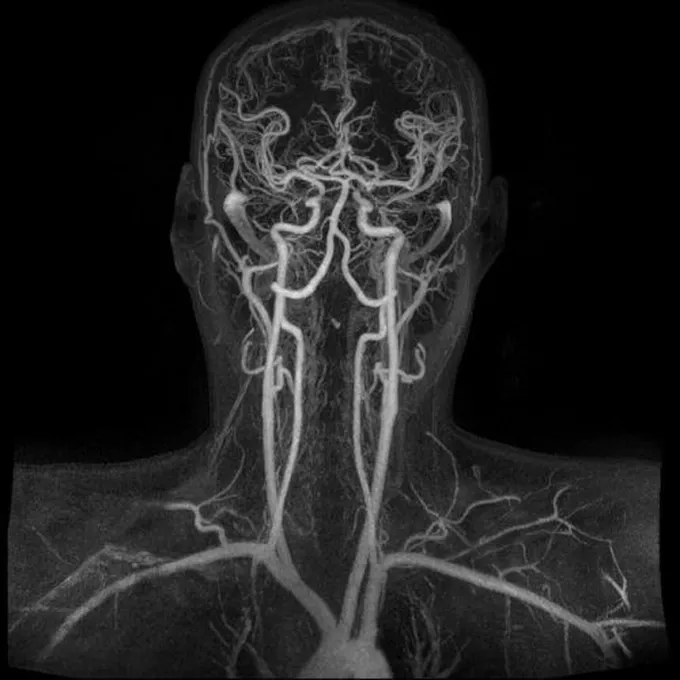
Vascular Anatomy of the Human Brain
 The Brain Needs a Lot of Energy:
The Brain Needs a Lot of Energy:
- The brain requires a tremendous amount of energy and oxygen to function properly.
- This is delivered through a complex system of arteries and veins.
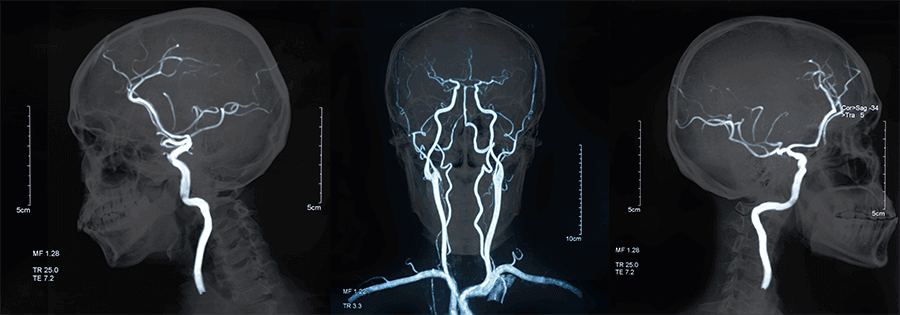
Blood Supply System:
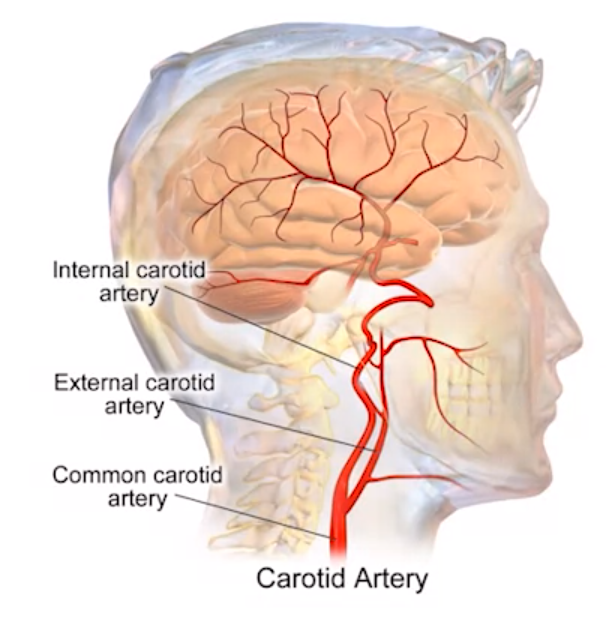
- The internal carotid artery is the main supplier of blood to the brain.
- It originates from the aorta and splits from the common carotid artery.
- The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and skull.
- The internal carotid arteries lead to the Circle of Willis.
Circle of Willis:
-
This is a ring-like structure formed by arteries at the base of the brain.
-
It acts as a distribution hub for blood flow to different brain regions.
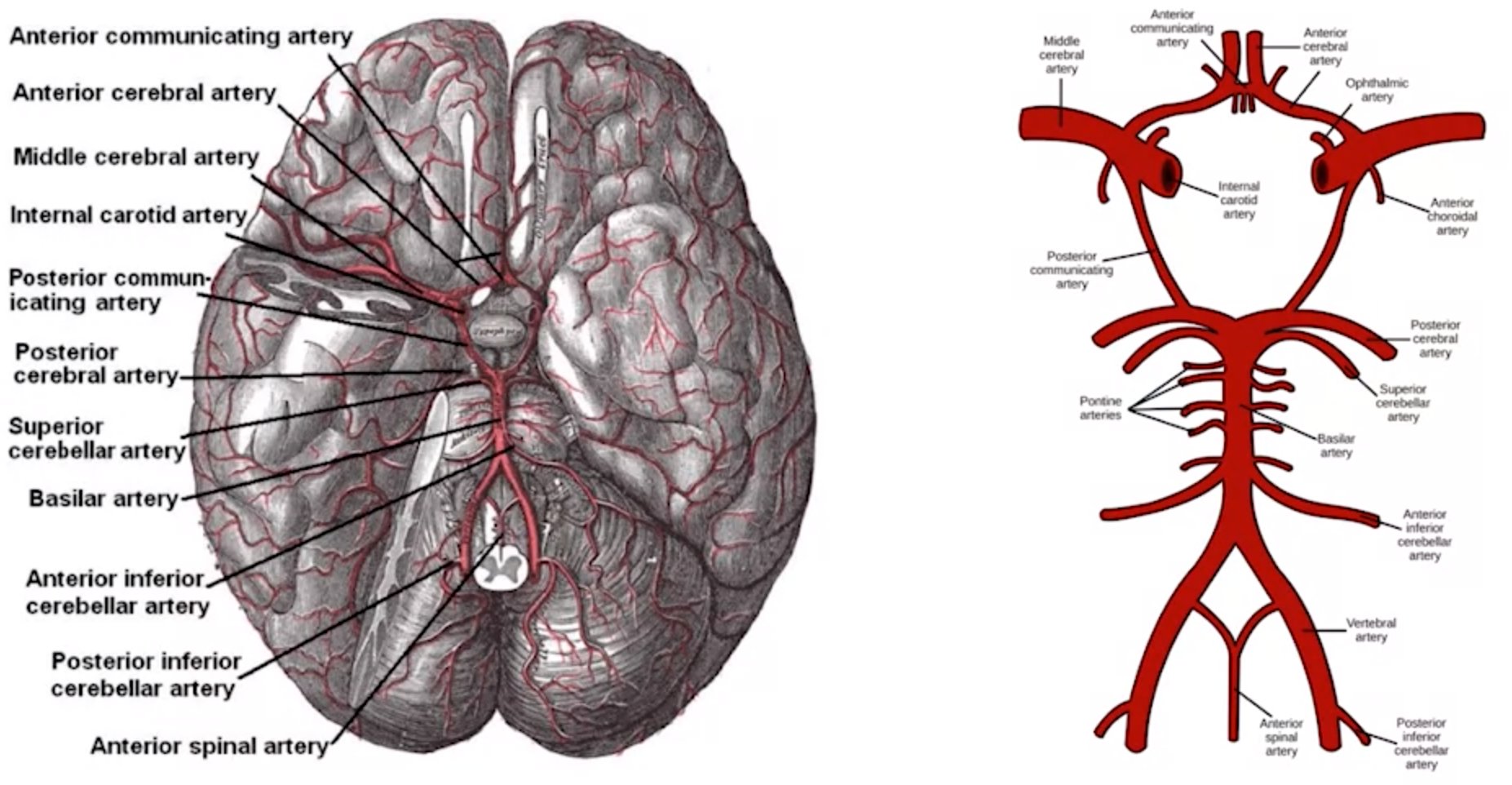 Blood Distribution from the Circle of Willis:
Blood Distribution from the Circle of Willis: -
Several arteries and veins branch out from the Circle of Willis, each supplying specific brain areas.
- Listed arteries include:
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Middle cerebral artery
- Posterior cerebral artery
- Superior cerebellar artery
- Pontine arteries
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Vertebral artery
- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Listed arteries include:
Cortical Vascular Territories:
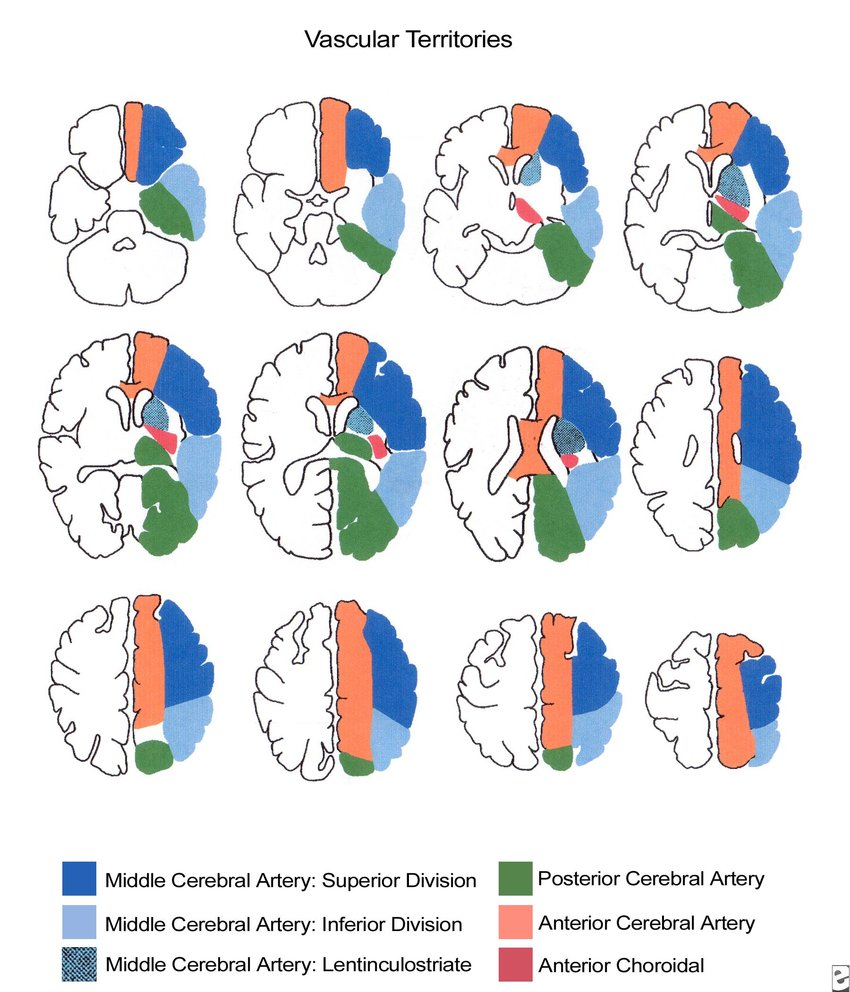
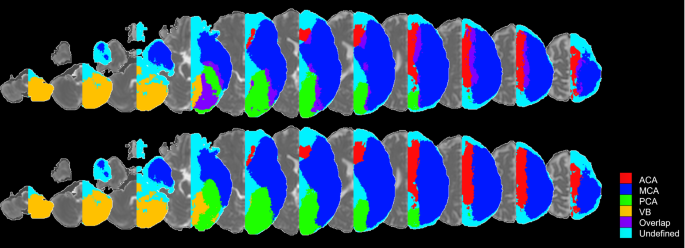
- Specific brain regions (cortical territories) are supplied by dedicated arteries from the Circle of Willis.
- These territories have defined boundaries with minimal overlap.
- This specific blood supply is important for neuroimaging techniques.
[!Explore More]