Higher Cognitive Functions
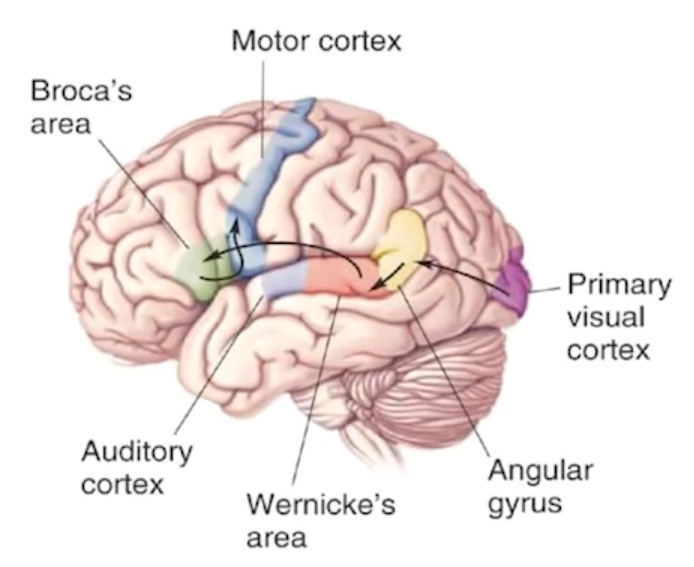
Language:
- Broca’s area: located in the inferior frontal gyrus, responsible for expressive language (speaking and writing). Damage leads to Broca’s aphasia (inability to produce fluent speech).
- Wernicke’s area: located in the superior temporal gyrus, responsible for receptive language (understanding spoken and written language). Damage leads to Wernicke’s aphasia (inability to understand language).
Memory:
-
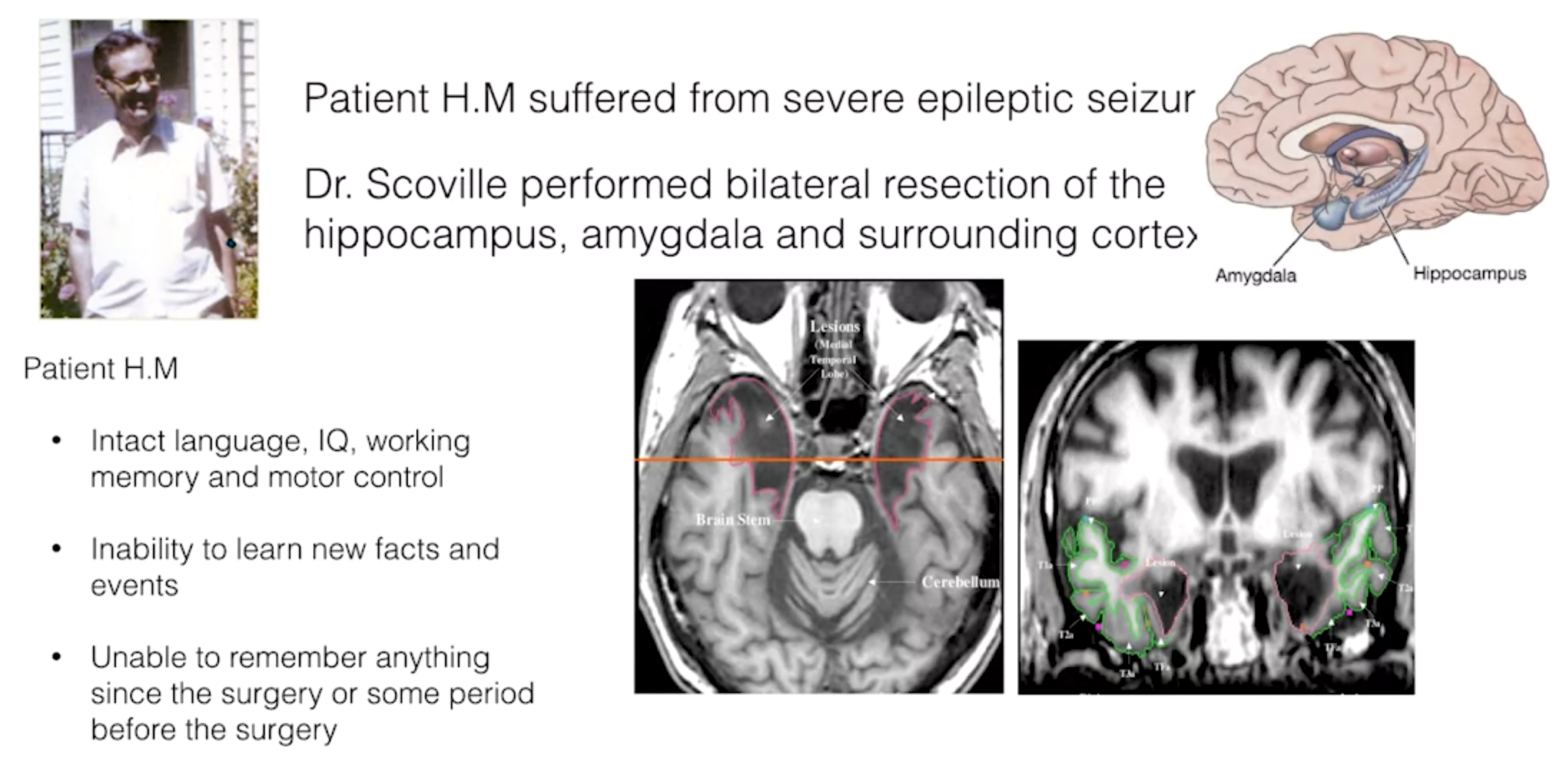
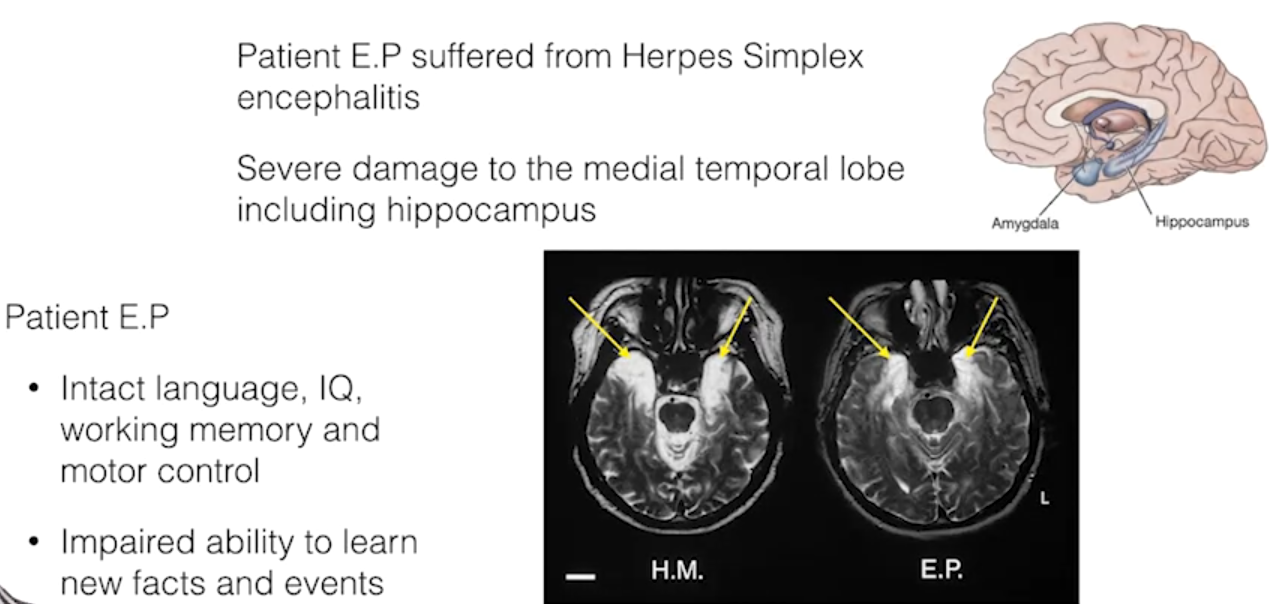
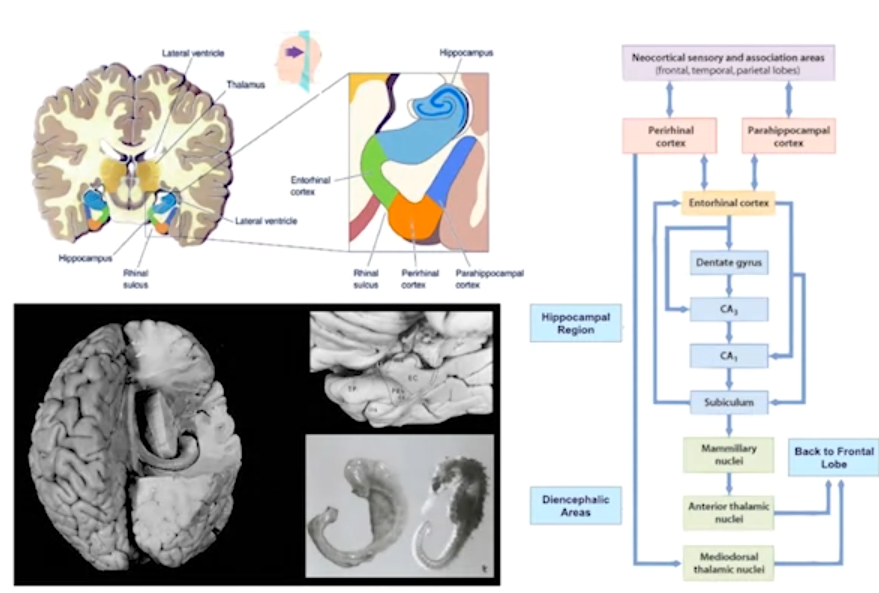
Medial temporal lobe, including the hippocampus: critical for forming new long-term memories, especially episodic memories (facts and events).
-
H.M. case study: patient with bilateral medial temporal lobe damage who could not form new memories but had normal working memory and motor skills.
-
-
-
Brenda Milner: proposed multiple memory systems based on H.M.’s case.
-
Basal ganglia: also involved in some forms of memory, particularly motor learning and habit formation.
The brain has multiple systems that support memory function, including:
- Medial temporal lobe: This area is involved in processing long-term memories
- Hippocampus: This structure is known to be critical for consolidation of memories from short-term to long-term storage
- Amygdala: This area is involved in processing emotions, and plays a role in storing emotional memories
- Basal ganglia: These structures are involved in habit formation and procedural memory, which is the memory of how to perform actions
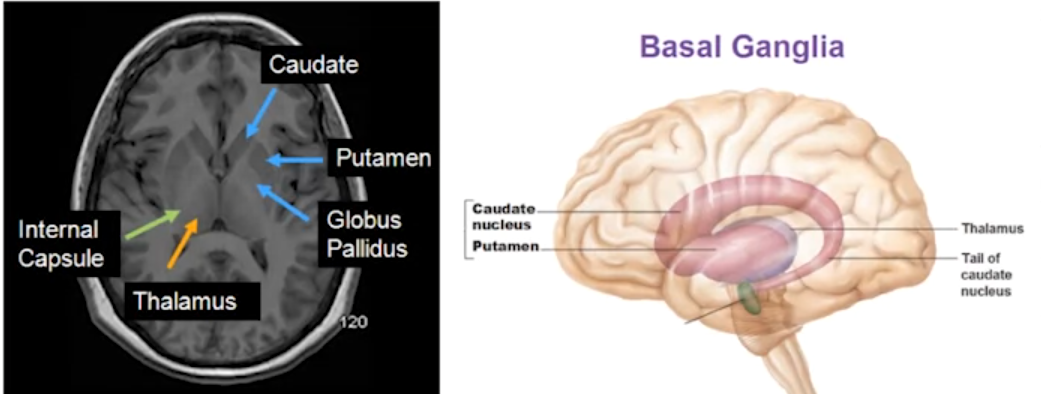 The parts of the basal ganglia:
The parts of the basal ganglia: - Striatum: Involved in reward, reinforcement, and some forms of learning
- Caudate nucleus: Involved in fine motor planning and movements
- Putamen: Involved in fine motor planning and movements
- Globus pallidus: Involved in some forms of learning
Other Cognitive Functions:
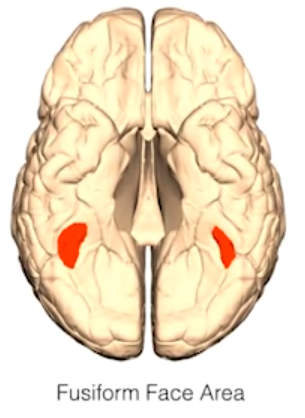
- Fusiform face area: critical for recognizing faces. Damage leads to prosopagnosia (inability to recognize faces).
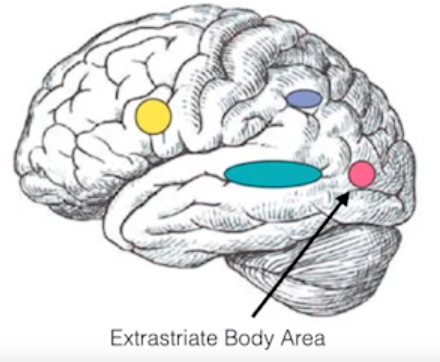
- Extrastriate body area: important for recognizing body parts.
General Points:
- Brain damage can reveal the function of specific brain regions.
- Different brain regions support different cognitive functions.
- There are multiple memory systems in the brain.