 Title: Types of Intracranial Bleeds
Title: Types of Intracranial Bleeds
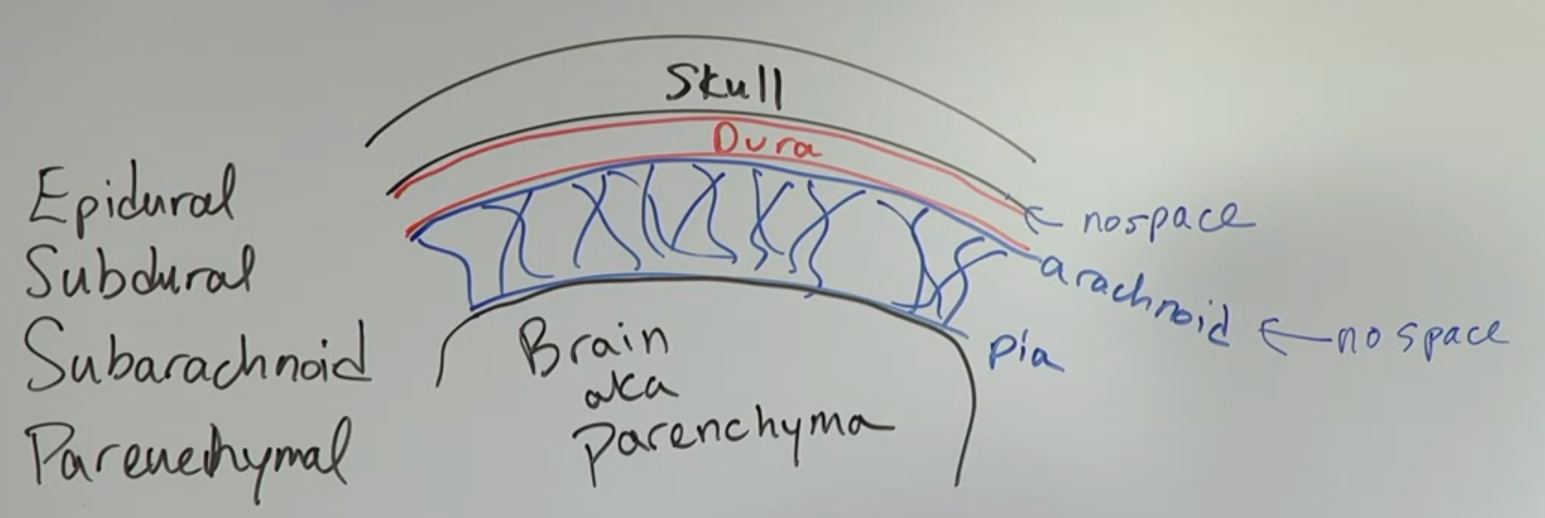
I. Limited Intracranial Space
- Bleeds within the cranium have serious consequences due to restricted space
Anatomical Layers
- Skull
- Dura (tough outermost membrane)
- Arachnoid
- Pia
- Brain Parenchyma (brain tissue)
Potential Bleed Locations
-
Epidural Bleed (between skull and dura)
- Epidural/Extradural hematomas
- Extremely dangerous, often fatal if untreated
- E.g. Caused Natasha Richardson’s death
- Lucid interval before deterioration
-
Subdural Bleed (between dura and arachnoid)
- Subdural hematomas
- Can range from asymptomatic to life-threatening
- More common in elderly
-
Subarachnoid Bleed (in cerebrospinal fluid space)
- Excruciating headache
- Very dangerous, can be fatal
- E.g. Philip Hughes - vertebral artery rupture
-
Intraparenchymal/Intracerebral Bleed
- Hemorrhagic stroke within brain tissue