Motor Neurons and Muscle Fibers
This lecture segment explains the connection between motor neurons and the different types of skeletal muscle fibers.
Key Points:
- Different motor neurons innervate different types of muscle fibers.
- There are three main types of motor neurons:
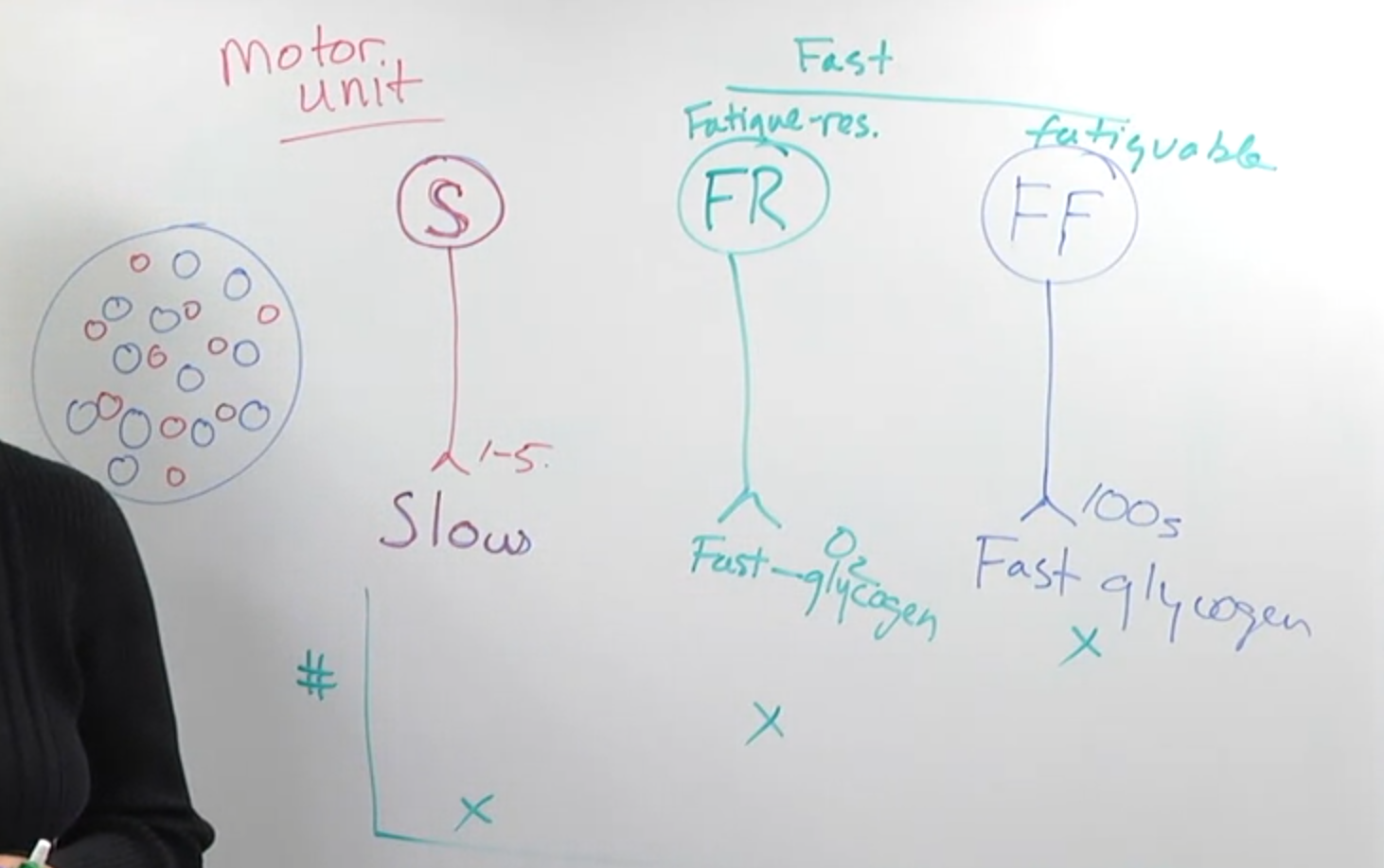
- Slow motor neurons: Innervate slow muscle fibers for sustained contractions.
- Fast fatigue-resistant motor neurons: Innervate fast muscle fibers that can use both oxygen and glycogen for contractions lasting around 30 minutes.
- Fast fatigable motor neurons: Innervate fast muscle fibers reliant solely on glycogen, leading to fatigue in 3-5 minutes.
Motor Units:
- A motor unit consists of a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates.
- The number of muscle fibers per motor unit varies:
- Slow motor neurons innervate few muscle fibers.
- Fast fatigue-resistant motor neurons innervate more muscle fibers.
- Fast fatigable motor neurons innervate the most muscle fibers.
Impact on Movement and Disease:
- Recruitment of different motor neuron types allows for smooth movements.
- In diseases like polio, motor neuron death leads to muscle weakness because the denervated muscle fibers cannot function.
- Post-polio syndrome might arise due to overworked remaining motor neurons struggling to compensate for lost ones.
 Orderly Recruitment
Orderly Recruitment