Key Ideas:
-
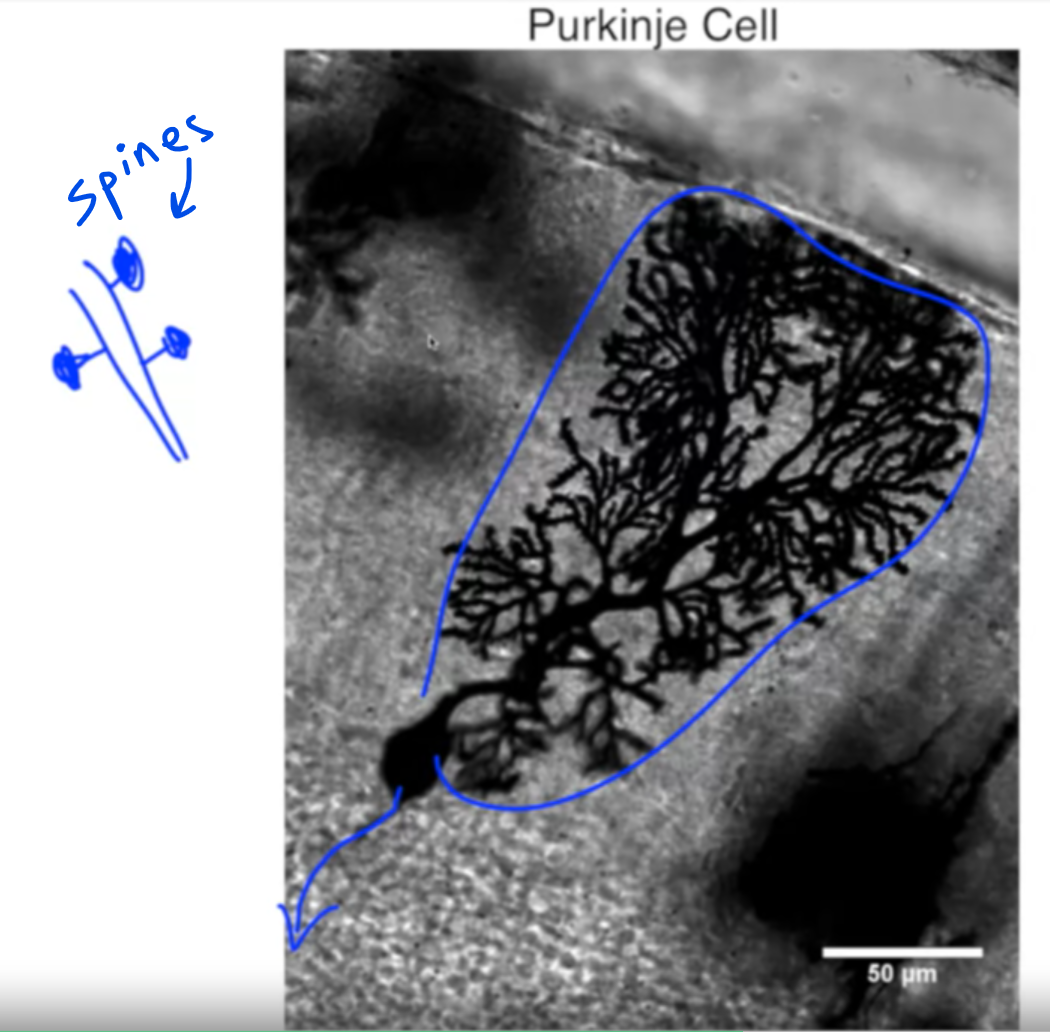
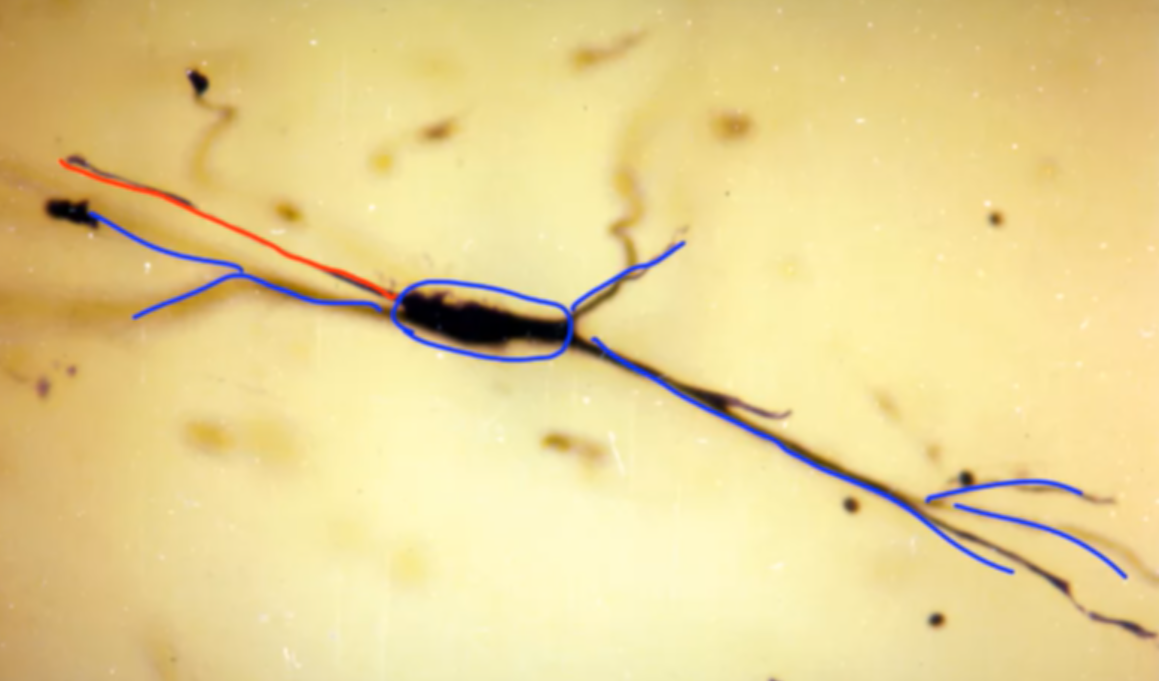
Neuronal Diversity: Neurons exhibit significant diversity in their appearance, even within the same nucleus or location.
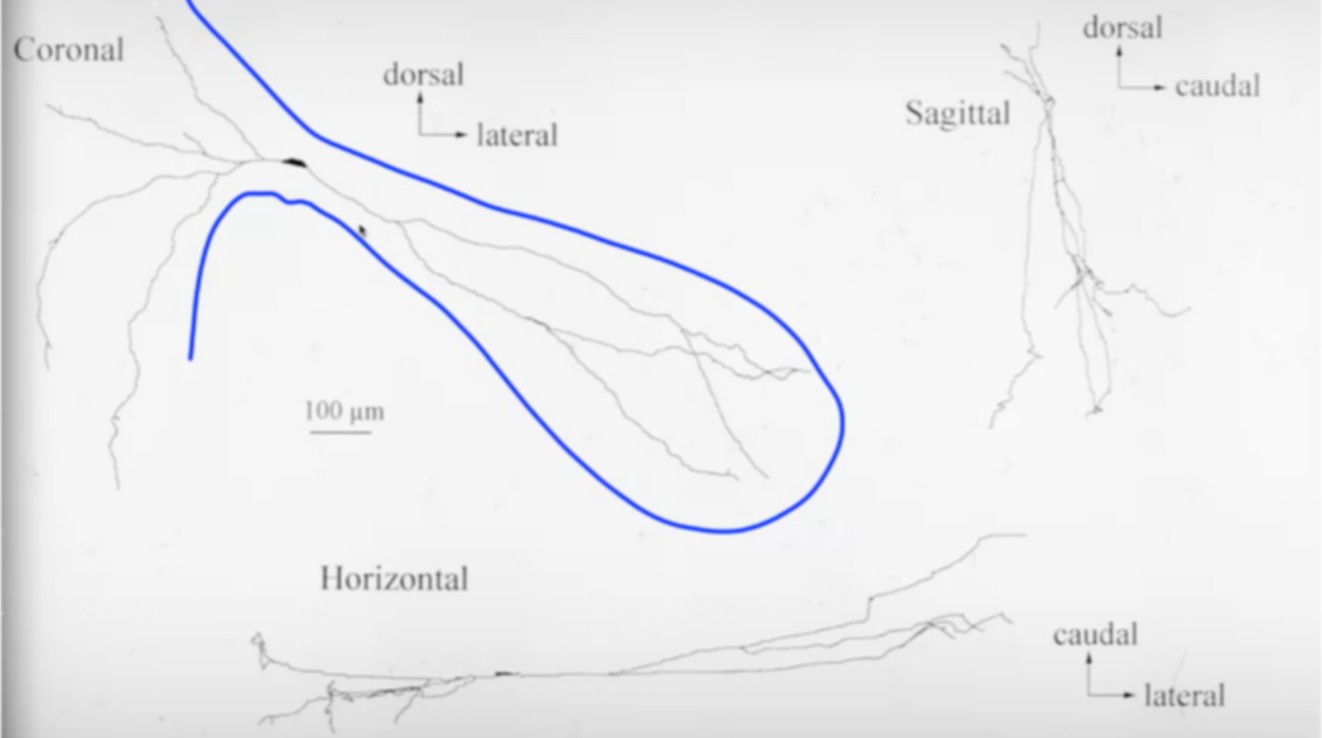
- Various reconstructions showcase the unique morphology of different neurons, highlighting differences in soma size, dendritic arbor complexity, and axonal structure.
- Neurons within the same location display distinct characteristics, despite sharing the same address.
-
Axonal and Dendritic Variability: Neurons vary in the size and shape of their dendritic arbors and axons, influencing their capacity to gather and transmit information.
- Diverse dendritic arbors determine the volume from which neurons collect information, with some neurons having elaborate structures while others are simpler.
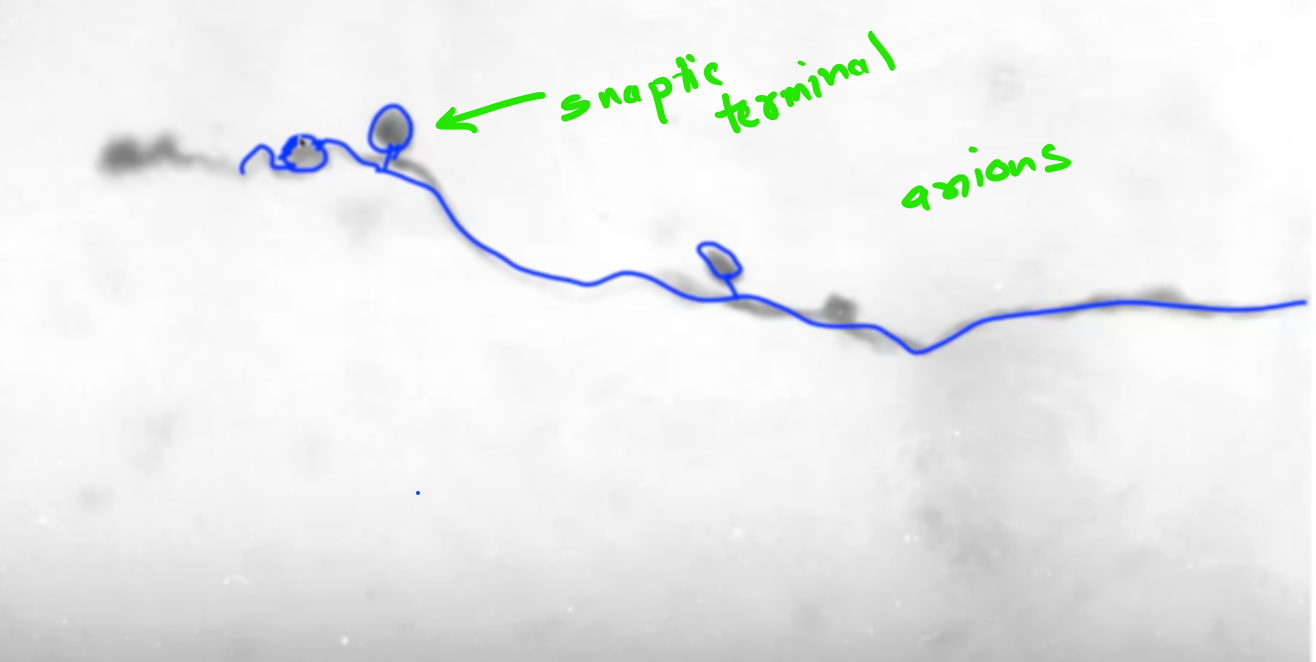
- Axonal morphology differs among neurons, with variations in branching patterns and synaptic terminals.
-
Connectivity and Function: Neurons differ not only in appearance but also in connectivity and function.
- Inputs and outputs of each neuron vary, determining which neurons it communicates with and receives signals from.
- Excitability levels vary among neurons, influencing their propensity to generate action potentials.
- Neurotransmitter usage varies, affecting the speed and nature of neuronal communication.
-
Comparison to Stars: Neurons are likened to stars in their uniqueness, with each neuron possessing its own distinct characteristics and functions.
- Introduction to the
 -
-