The Brain’s Structure and Connectivity
This lecture focused on the development of the brain’s connectivity between its major parts.
Key Points:
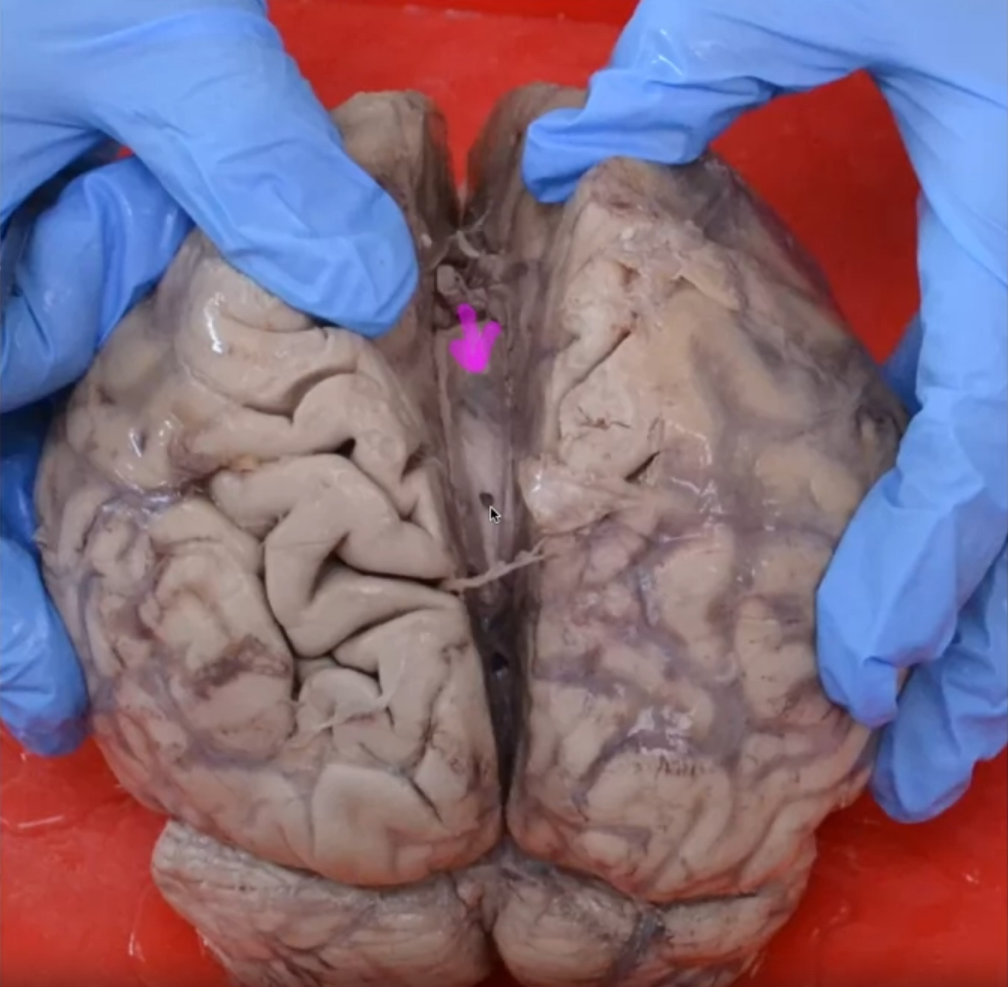
- The telencephalon, initially two separate hemispheres, expands and covers the other brain regions.
- In an adult brain, two important structures bridge these regions:
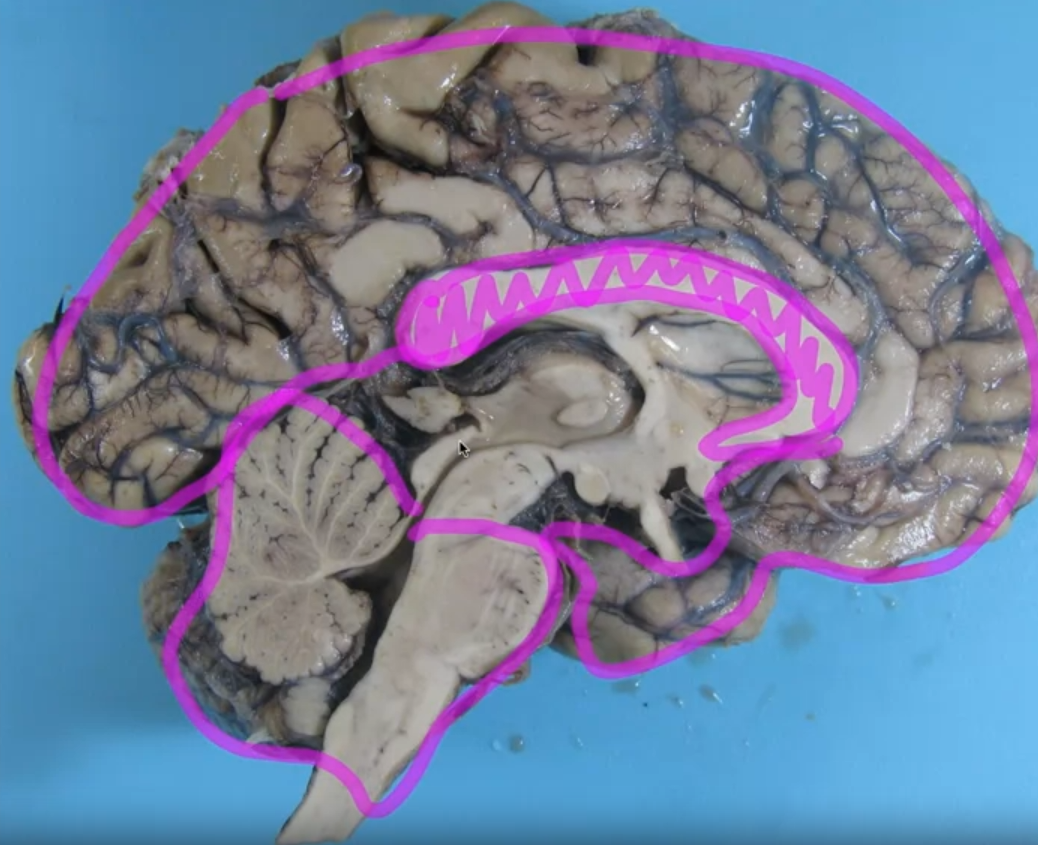
- Corpus callosum: Connects the two hemispheres, enabling communication between them.
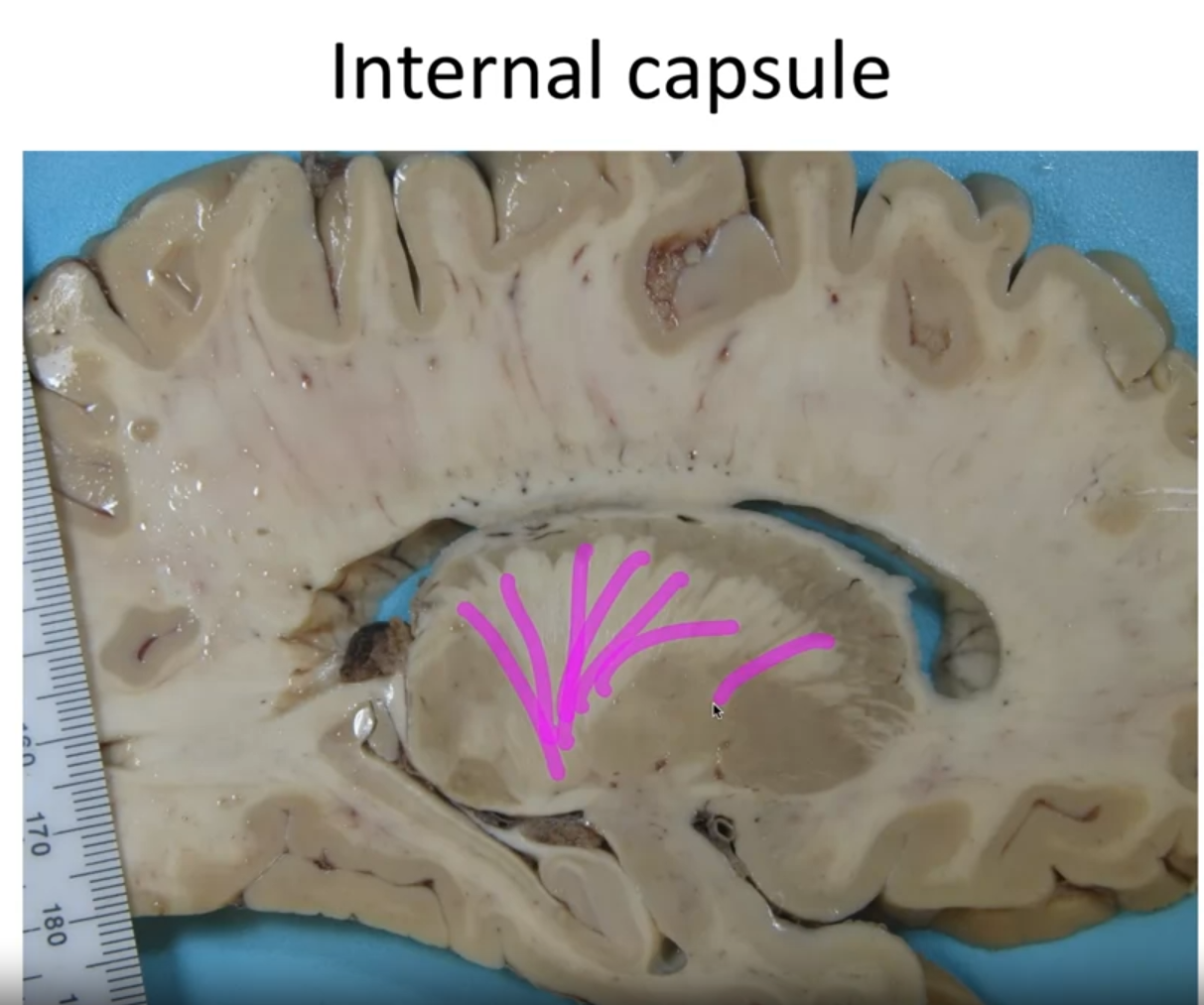
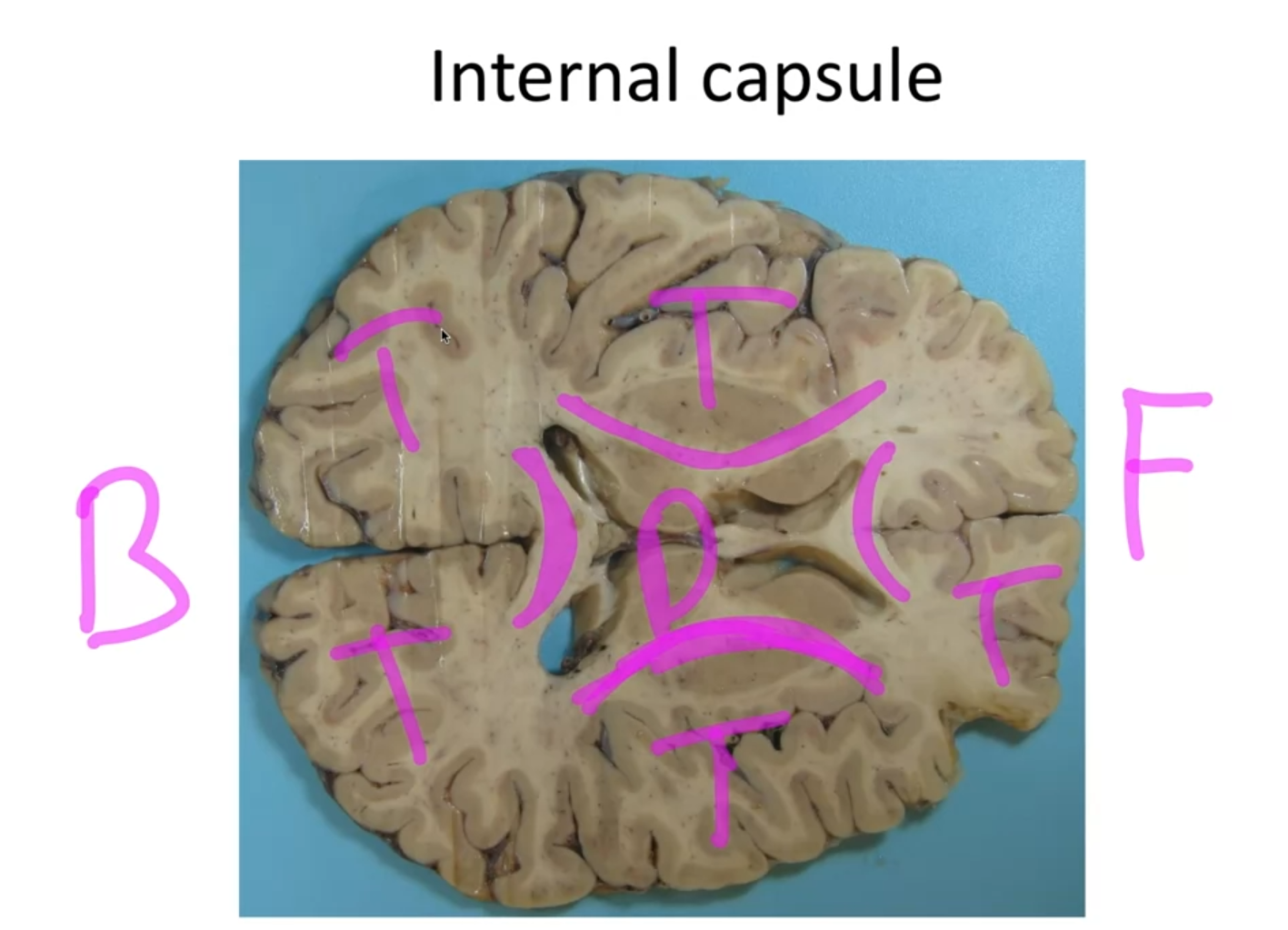
- Internal capsules: Connect the telencephalon to the diencephalon. They carry crucial information, including motor information to the muscles.
Brain Connectivity:

-
Initially, the hemispheres are separate structures.
-
The corpus callosum develops later, allowing communication between the hemispheres.
-
The internal capsules connect the telencephalon (cerebral cortex) to the diencephalon. They carry information, including motor signals that control muscles on the opposite side of the body.
 (not a mid sagittal cut, it is para sagittal cut)
(not a mid sagittal cut, it is para sagittal cut)
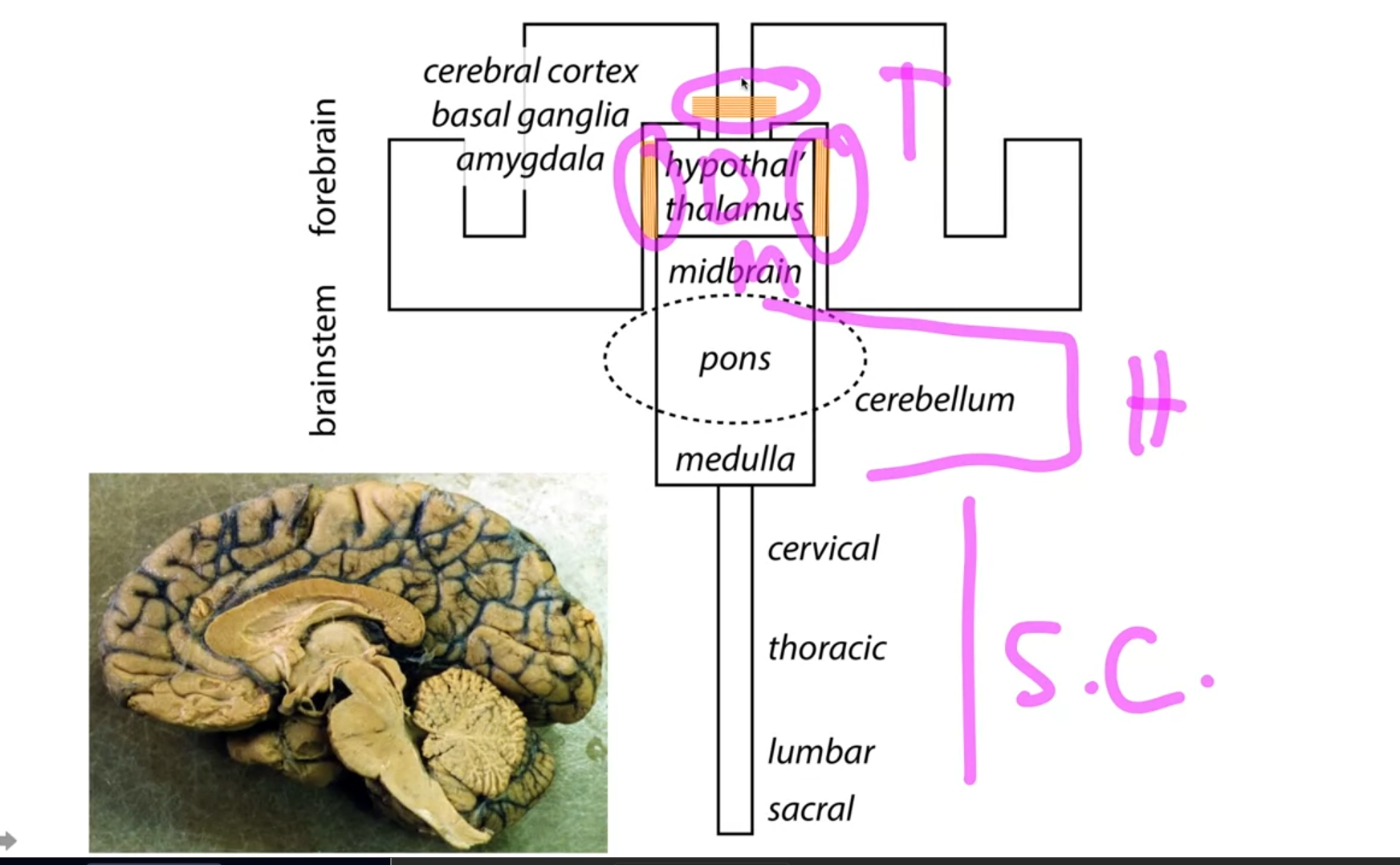
 Brain Regions:
Brain Regions:
-
Spinal cord: Carries signals between the brain and the body.
-
Hindbrain: Includes the pons, medulla, and cerebellum. Involved in basic functions like breathing and heart rate.
-
Midbrain: Relays sensory and motor information.
-
Diencephalon: Contains structures like the thalamus, which relays sensory information to the cortex.
-
Telencephalon: Makes up the cerebrum, the largest part of the brain. The outer layer is the cerebral cortex, responsible for higher functions like thinking and memory.
Additional Notes:
- The space in the center of the brain (ventricles) contains cerebrospinal fluid and is not brain tissue.
- A midsagittal cut divides the brain in half along the midline.
- A parasagittal cut is similar to a midsagittal cut but slightly off-center.
- A horizontal cut divides the brain parallel to the ground.
Final Diagram:
The lecture concludes by introducing a simplified brain diagram that will be used throughout the course. This diagram shows the major brain regions and their connections via the corpus callosum and internal capsules.