Neurons and Neurotransmitters
This lecture dives into neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers used by neurons to communicate:
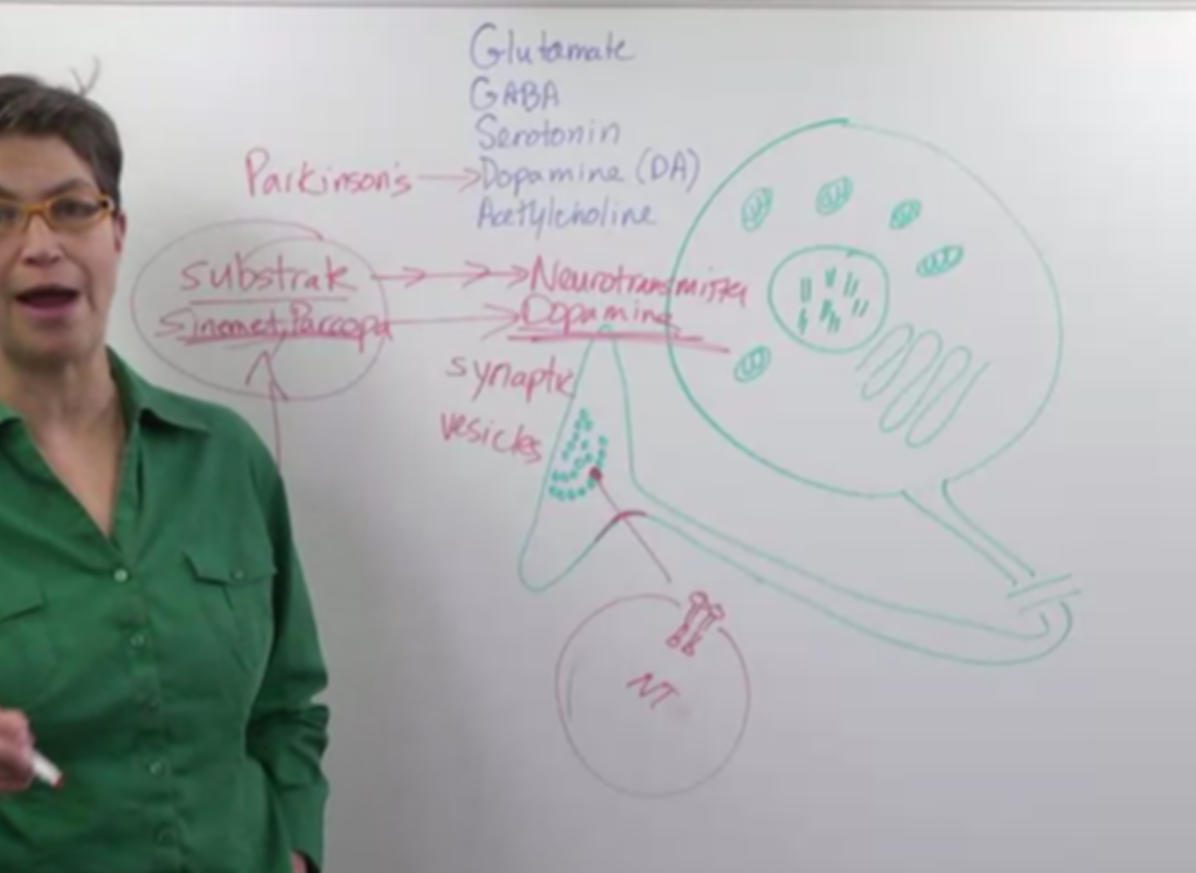
Neurotransmitters:
- Chemical messengers used by neurons to communicate across synapses.
- Packaged in tiny membrane-bound spheres called synaptic vesicles.
- Examples include glutamate, GABA, serotonin, dopamine, and acetylcholine.
Importance of Packaging:
- Ensures neurotransmitters are concentrated and readily available for release.
- Plays a role in targeting specific types of neurons.
Therapeutic Applications:
- Understanding neurotransmitter synthesis is crucial for developing treatments.
- In Parkinson’s disease, dopamine-producing cells die, leading to a deficiency.
- Levodopa (Sinemet, Parcopa) is a precursor (substrate) for dopamine synthesis used to alleviate symptoms.
- By flooding the system with levodopa, even a small amount of dopamine production can improve the patient’s condition.
Key Points:
- Neurotransmitters are essential for communication between neurons.
- Packaging in vesicles is crucial for efficient and targeted signaling.
- Understanding neurotransmitter systems paves the way for developing treatments for neurological disorders.
Neurons: Neurotransmitter Release
This lecture explains how an action potential triggers the release of neurotransmitters at the synapse:
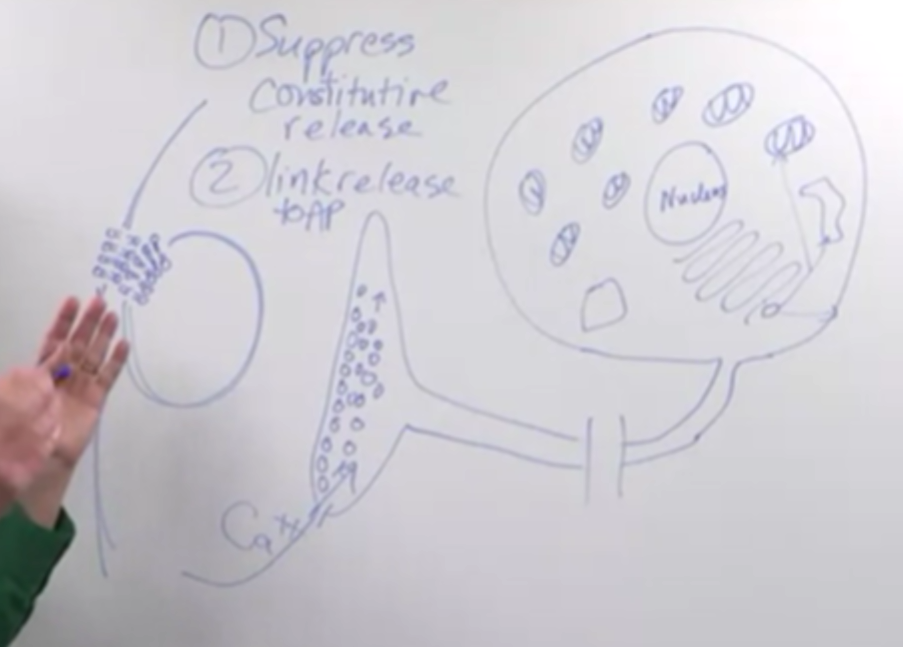
Problem:
- Neurons need to prevent random release of neurotransmitters from vesicles.
- They also need to link neurotransmitter release to the arrival of action potentials.
Solution:
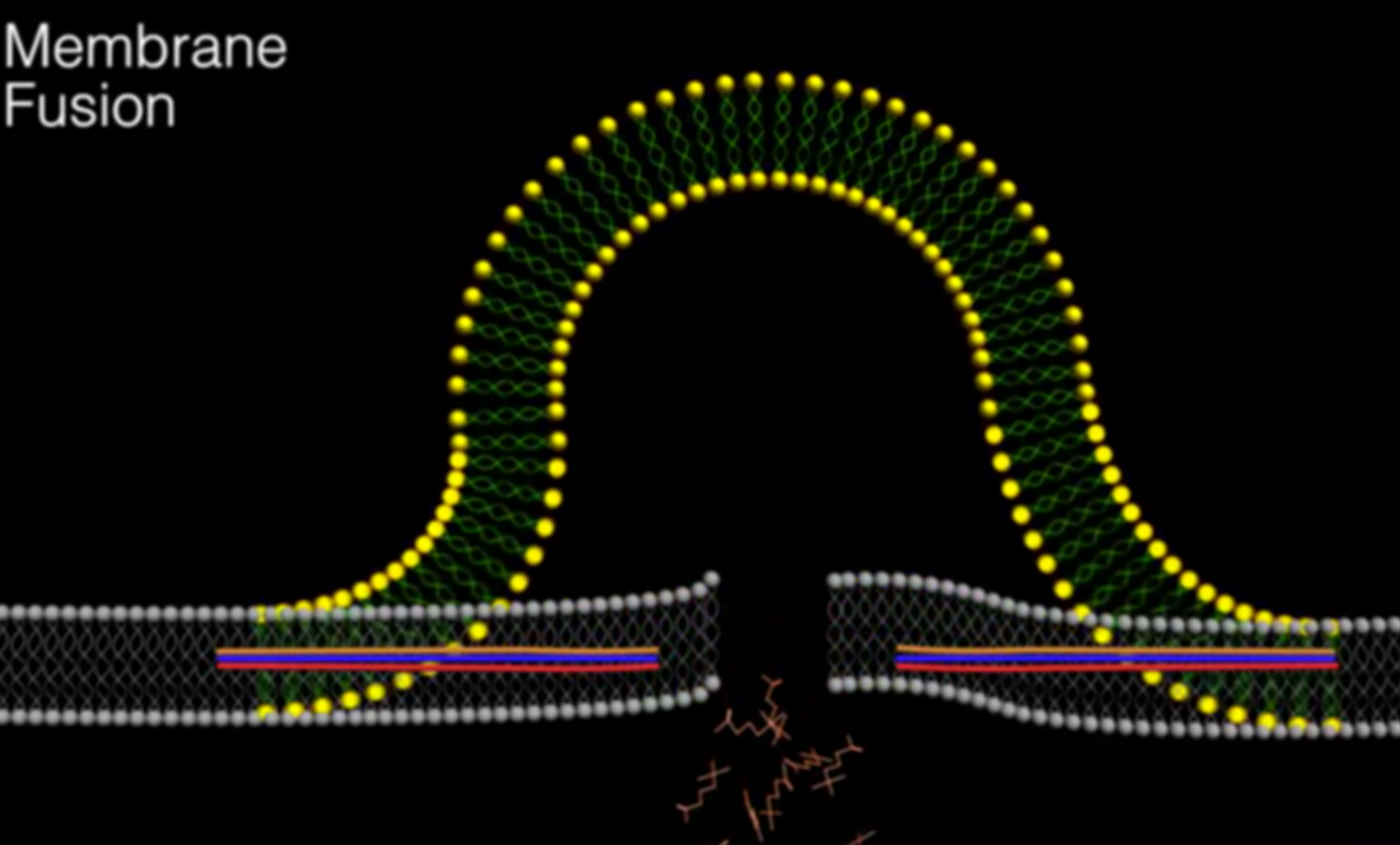
- Suppression of constitutive release: A molecule within the terminal actively prevents spontaneous fusion of vesicles with the cell membrane.
- Linking release to action potential:
- Action potential arrival causes a rise in membrane potential.
- This opens calcium channels, allowing calcium ions to enter the terminal.
- Increased calcium concentration triggers the fusion of vesicle membranes with the cell membrane.
- Neurotransmitters are released through the fused membrane.
Key Points:
- Only action potentials trigger neurotransmitter release, ensuring a controlled communication system.
- Calcium ions act as a signal for vesicle fusion, linking electrical activity to chemical signaling.
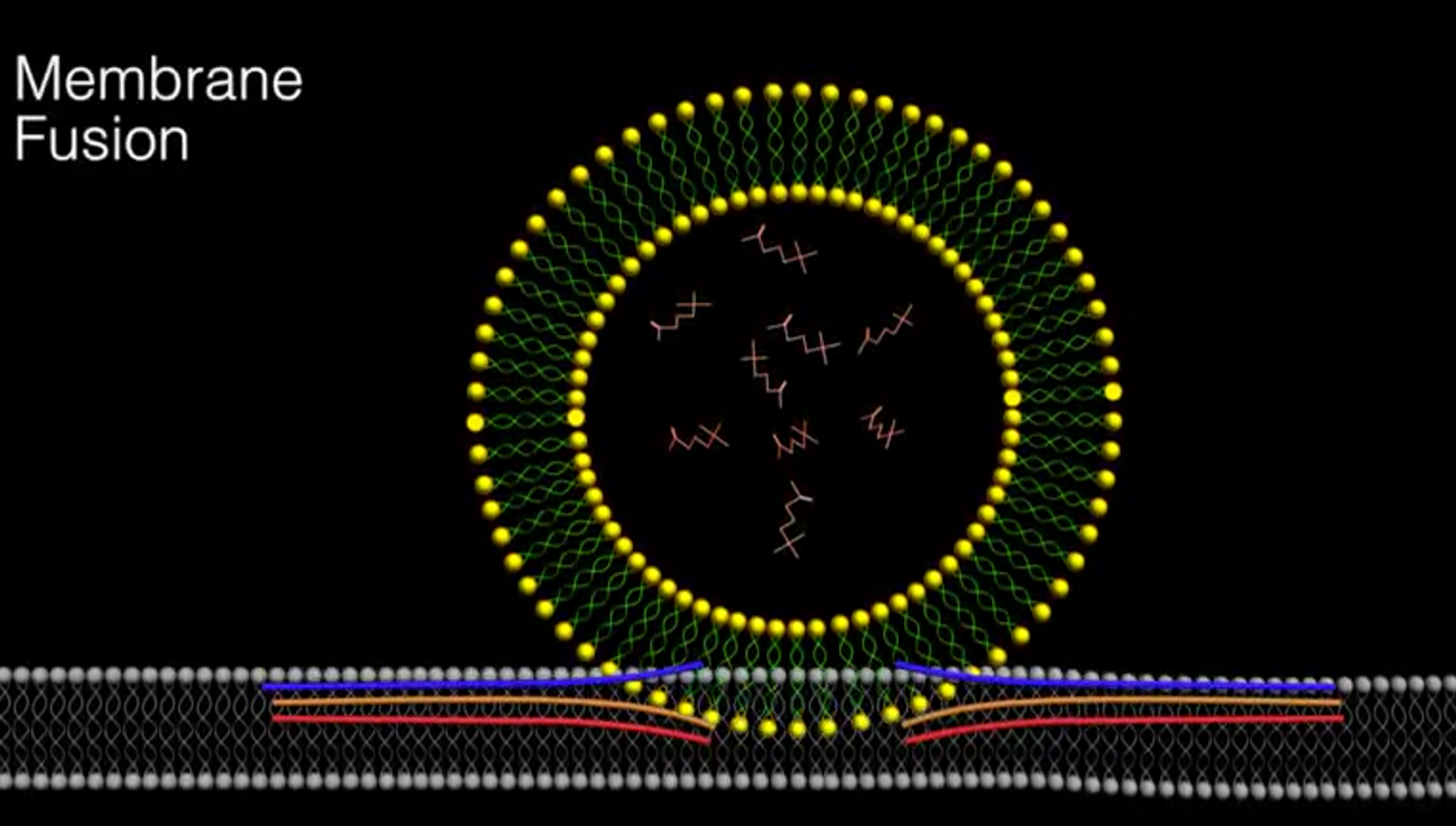
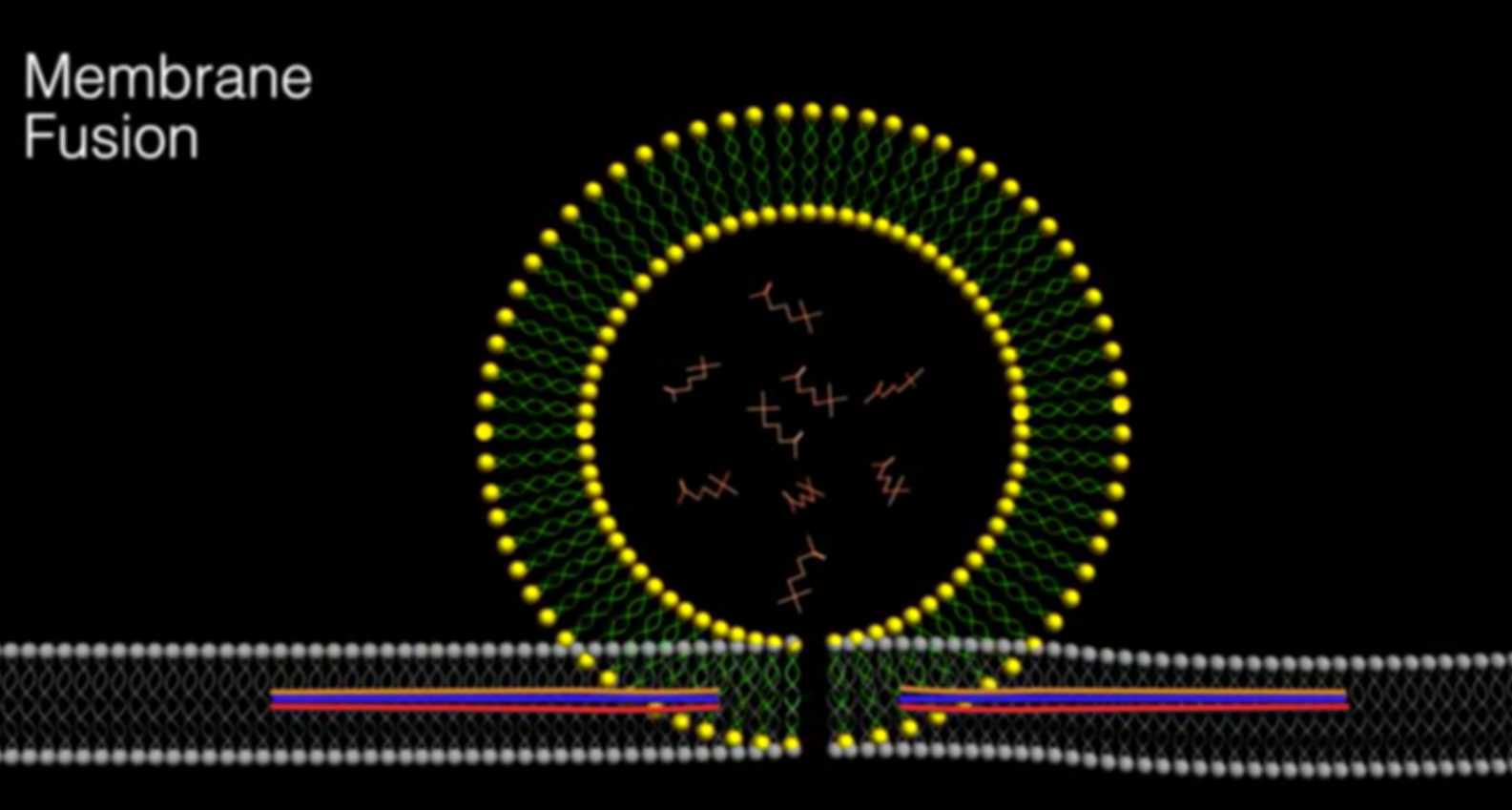
 Botox
Botox