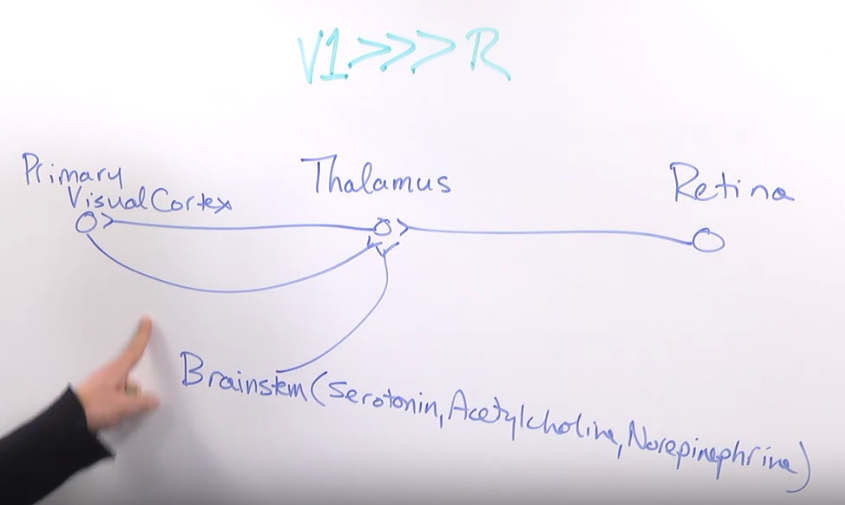
The Role of the Thalamus
- Visual information processing pathway: Retina → Thalamus → Primary visual cortex.
- Thalamus as a translator: Acts as a relay station for visual information.
- Unexpected input: The thalamus receives significant input from the visual cortex and brainstem, in addition to the retina.
- Cortical influence: Input from the visual cortex to the thalamus is much stronger than retinal input.
- Orwellian analogy: Some inputs (retinal) are more equal than others (cortical and brainstem).
The Impact of Expectations
- Purpose of cortical input: Informs the brain about what to expect to see.
- Perceptual habits: Expectations help process visual information faster.
- Example: Recognizing a familiar person with minimal visual cues.
- Advantages of expectations: Saves processing time and facilitates quicker perceptual judgments.
Disadvantages of Expectations
- Stereotypes and biases: Expectations can reinforce existing beliefs and hinder perception of new information.
- Difficulty in detecting change: Reliance on expectations can make it harder to notice differences.
- Example: Difficulty noticing changes in colleagues’ appearance.
Conclusion
- General principle: The brain favors established patterns of thought and perception.
- Trade-off: Efficiency versus accuracy.
- Next topic: How attention controls our perception of the world.
Key Points:
- The thalamus plays a crucial role in visual perception, but its function is influenced by inputs from other brain regions.
- Expectations shape our perception of the world, offering advantages in terms of speed but also leading to potential biases.
Learned Perceptual Habits
- Development of expertise: With practice, individuals can become experts at identifying specific visual patterns.
- Example: Where’s Waldo? Initial difficulty in locating Waldo gradually decreases with repeated attempts.
- Real-world applications: Finding mushrooms, identifying bird species, recognizing car models.
- Efficiency: Learned perceptual habits allow for rapid identification with minimal information.
The Role of Attention
- Attention as a prerequisite: Effective perception relies on focused attention.
- Hemispacial neglect: A neurological condition demonstrating the importance of attention.
- Limited awareness: Without attention, objects or information may not be perceived.
Conclusion
- Learned perceptual habits and attention are interconnected and crucial for visual processing.
- Attention is a complex process requiring further research.
Key Points
- Practice enhances visual pattern recognition.
- Expertise allows for efficient perception of specific stimuli.
- Attention is essential for conscious perception.