Brainstem Organization of Saccades: A Closer Look
This lecture explains how the brainstem coordinates horizontal gaze shifts, the simplest form of saccades.
-
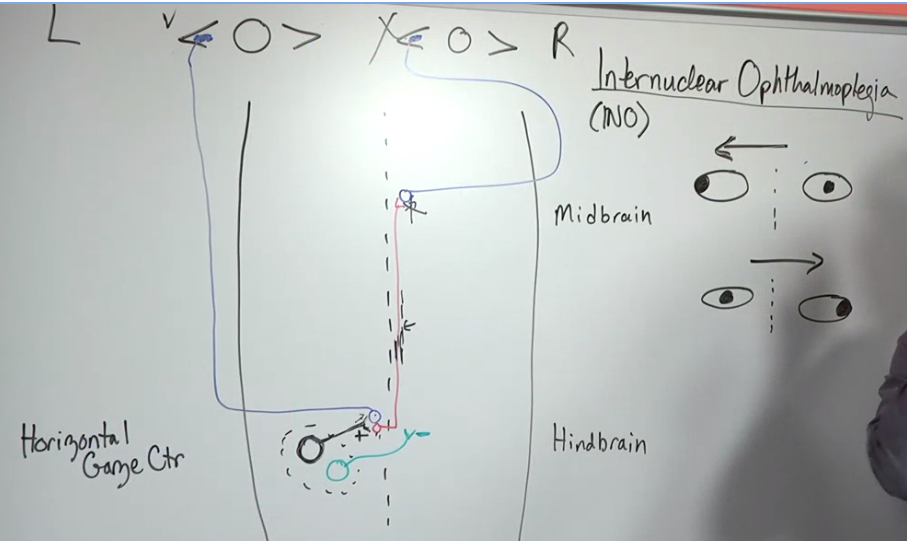
Horizontal Gaze Center: Located in the pons, this brain region contains neurons responsible for initiating horizontal eye movements.
-
Neural Circuit for Leftward Gaze Shift:
- Excitatory neuron in the gaze center directly stimulates the motor neuron controlling the left lateral rectus muscle (responsible for abducting the left eye).
- Inhibitory interneuron ensures simultaneous activation of the right medial rectus muscle (adducting the right eye) for coordinated movement of both eyes.
-
Clinical Application: Damage to the myelin sheath (insulating layer) of these neural connections, as seen in multiple sclerosis, can disrupt this circuit. This can lead to internuclear ophthalmoplegia, a condition where one eye fails to move inwards during a gaze shift to the opposite side.
-
Next Lecture: The lecture will explore how the brain controls saccades.
 Controlling Saccades
Controlling Saccades