Key Ideas:
-
Myelin Function: Myelin is a fatty sheath that wraps around some axons, enabling faster transmission of nerve impulses.
-
Difference Between Myelinated and Unmyelinated Axons:
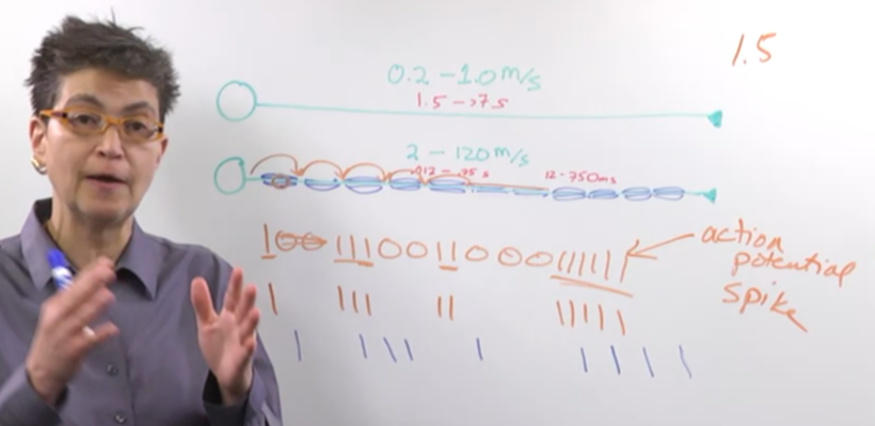
- Unmyelinated axons transmit information at a slower rate (0.2 to 1 meter per second), resulting in slower response times.
- Myelinated axons transmit information much faster (2 to 120 meters per second), allowing for rapid signal transmission.
-
Importance of Myelin:
- Myelinated axons allow for quick transfer of essential information, particularly important for tasks like maintaining balance and posture.
-
Neural Coding:
- Information transmission involves a series of 0s and 1s, akin to a computer code.
- The timing of these “spikes” or action potentials carries crucial information, forming the neural code.
-
Mechanism of Myelination:
- Myelin wraps around axons, facilitating rapid signal transmission.
- Action potentials “jump” between myelin sheaths, enhancing speed.
-
Consequences of Demyelination:
- Loss of myelin results in significantly slowed or failed transmission of nerve impulses.
- Demyelination leads to degraded information transfer, resulting in a garbled message to the receiving neuron.
-
Major Types of Demyelinating Diseases:
- In the next segment, focus will shift to two major types of demyelinating diseases, highlighting the impact of demyelination on neurological function.
Note Structure:
- Myelin Function
- Role in facilitating faster transmission of nerve impulses
- Difference Between Myelinated and Unmyelinated Axons
- Contrasting speeds of information transmission
- Importance of Myelin
- Essential for rapid response times, particularly in tasks like balance maintenance
- Neural Coding
- Information transmission as a series of spikes or action potentials
- Mechanism of Myelination
- Description of myelin wrapping around axons and its role in enhancing speed
- Consequences of Demyelination
- Impact of myelin loss on nerve impulse transmission and message clarity
- Major Types of Demyelinating Diseases
- Preview of upcoming focus on demyelinating diseases in the next segment