Introduction
- The human brain is vastly different from the brains of simpler animals like sharks and alligators.
- This difference is due to the expansion of the telencephalon, specifically the cerebral cortex.
The Telencephalon
- The telencephalon is the part of the forebrain that is responsible for higher-order functions like learning, memory, and thought.
- In humans, the telencephalon is the largest part of the brain.
- The expansion of the telencephalon is what allows humans to have complex behavior.
The Cerebral Cortex
- The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the telencephalon.
- It is made up of six layers of neurons and is only found in mammals.
- The cerebral cortex is responsible for most of the higher-order functions of the brain.
- The large surface area of the cerebral cortex is due to the presence of sulci (folds(valleys)) and gyri (convolutions(hills)).
Microcephaly
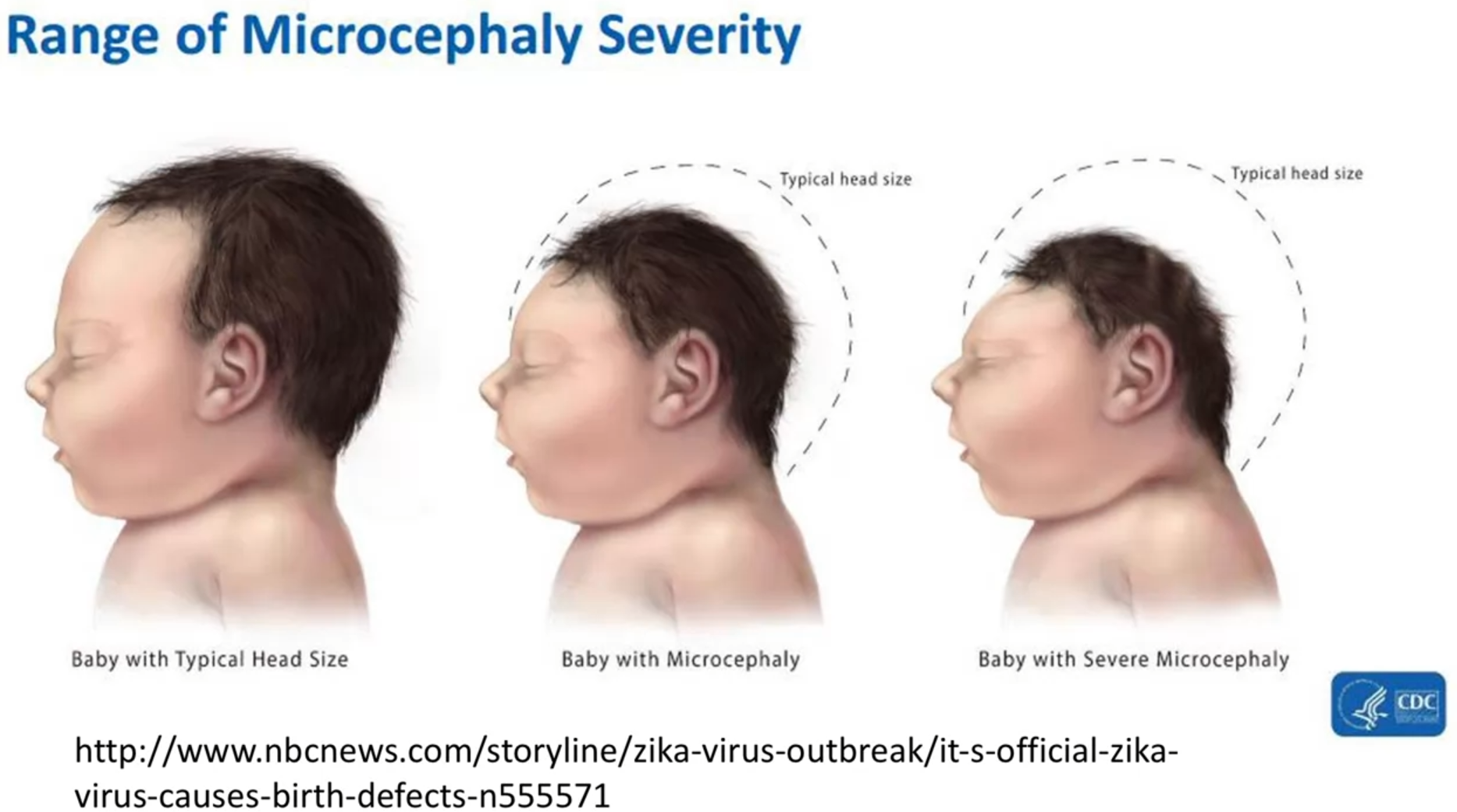
- Microcephaly is a condition in which the baby is born with a small head and brain.
- It can be caused by a variety of factors, including the Zika virus.
- The severity of microcephaly depends on when during gestation the infection occurs.
Additional Notes
- The lecture mentions that the neural tube forms by day 28 of human gestation.
- The lecture also mentions that the Zika virus is a mosquito-borne virus.
Conclusion
- The expansion of the telencephalon, particularly the cerebral cortex, is what allows humans to have complex behavior and is the foundation of our intelligence.
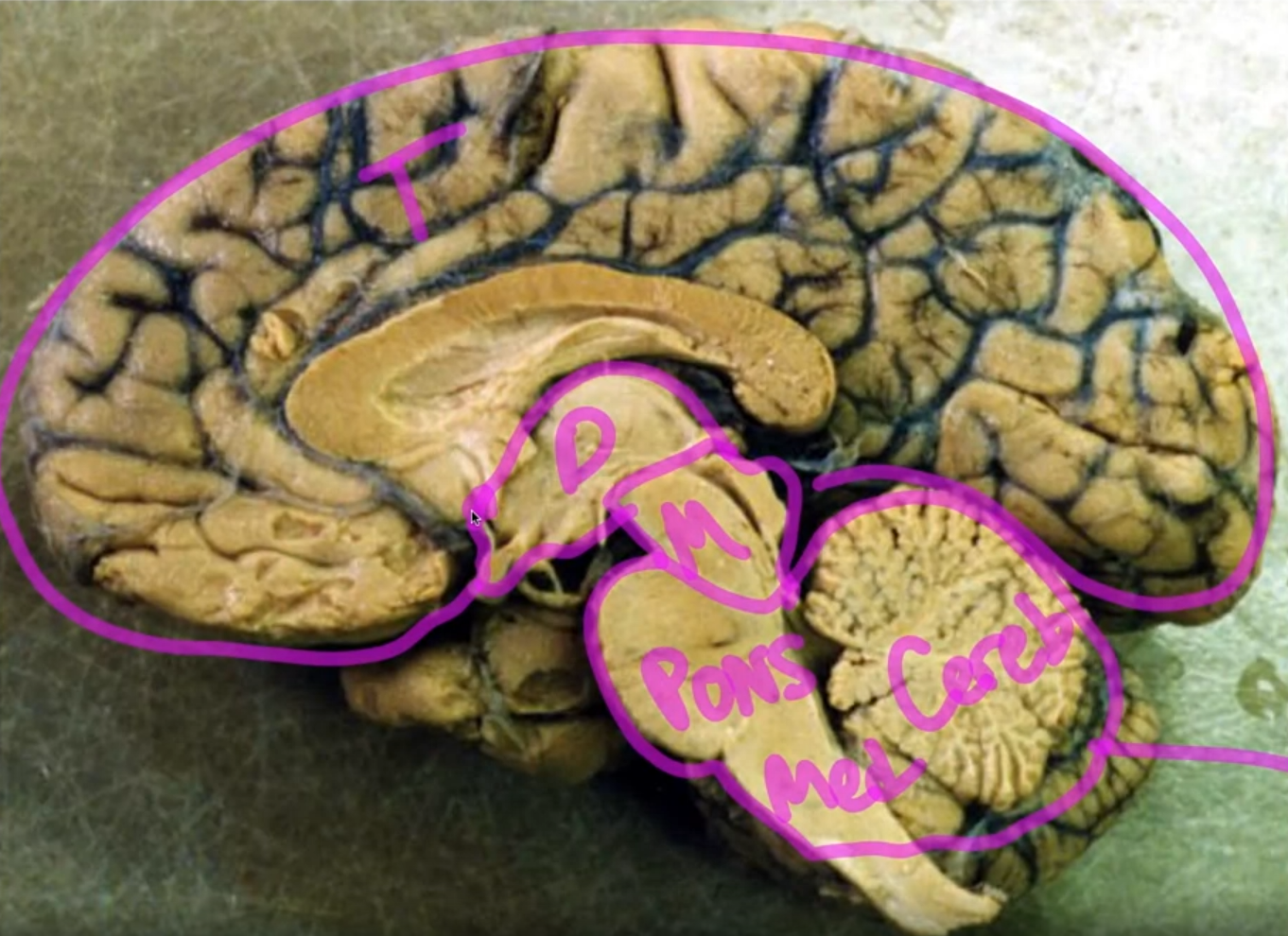
Hine brain = Cerebellum + Medulla + Pons Mid brain = small Diencephalon = small ( has optical nerves) Telencephalon = right & left ( biggest - envelops the rest of the brain)