Voluntary Movement Lecture Notes
** Impact of Damage to the Motor System**
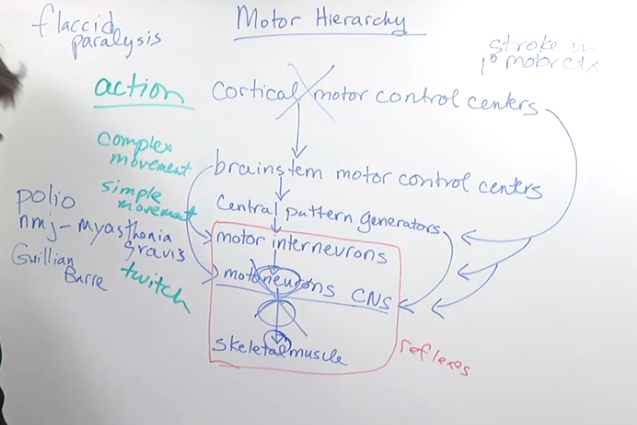
- The lecture explores how damage at different levels of the motor hierarchy affects movement.
Motor Neuron Damage:
- Caused by diseases like polio, Guillian-Barre syndrome, and neuromuscular junction problems.
- Disrupts the connection between motor neurons and muscles.
- Results in:
- Complete paralysis: No muscle movement is possible (flaccid paralysis).
- Loss of reflexes: Reflexes cannot occur without motor neuron stimulation.
- Muscle atrophy: Disuse leads to muscle weakness and shrinkage.
Cortical Motor Cortex Damage (Stroke):
- Damage to the primary motor cortex disrupts voluntary movement control.
- Reflexes: Can become exaggerated (hyperreflexia) due to disinhibition.
- Stereotyped movements: Can still occur (walking, chewing).
- Movements of self-expression: Impaired, especially for muscles controlled by the affected cortex area.
- Example: Difficulty lifting the left leg due to damage in the left motor cortex.
The Motor Hierarchy in Action:
- The lecture emphasizes the concept of the motor hierarchy as a top-down control system.
- Cortical motor control centers can influence:
- Brainstem motor control centers
- Central pattern generators
- Motor interneurons
- Motor neurons (limited direct connection)
- Information flow is primarily top-down (cortex to lower levels).
- Lower levels cannot directly communicate back to the cortex (with some exceptions).
Key Points:
- Damage location within the motor hierarchy determines the type of movement impairment.
- Motor neuron damage leads to complete paralysis and loss of reflexes.
- Cortical damage can cause hyperreflexia, preserve stereotyped movements, and impair voluntary control.
- The motor hierarchy functions in a top-down manner with limited feedback from lower levels.
Note:
- This section discusses the consequences of damage at different levels of the motor system. The concept of the motor hierarchy as a top-down control system is reinforced.