- How light enters the eye
- The retina and initial processing
- Pathways for interpreting visual information (what and where)
- How we learn to see
II. Visual Field
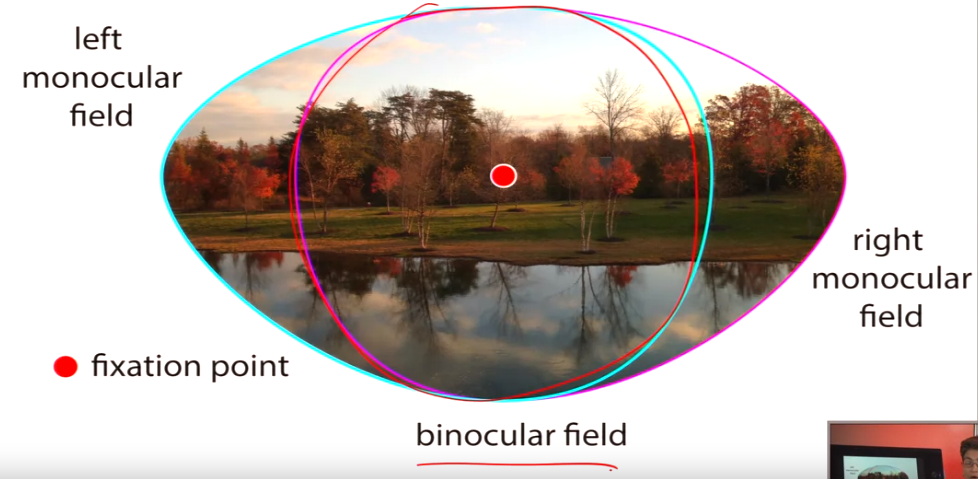
- Binocular field: Overlap between the visual information received by both eyes. This is the majority of the visual field.
- Monocular field: Crescent-shaped areas on the far left and right of vision where information is only received by one eye.
III. Light Entering the Eye
- The lecture will discuss how light interacts with the eye:
- Cornea: Transparent front layer that bends light
- Lens: Focuses light onto the retina
- Retina: Light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye
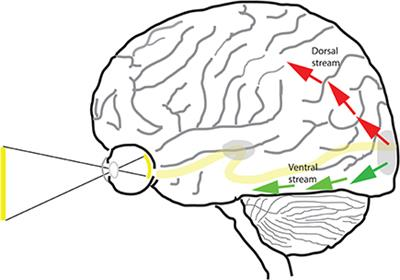
IV. Brain Processing
-
The lecture will illustrate the pathway visual information takes through the brain:
- Optic nerves: Transmit information from the eye
- Optic chiasm: Where some nerve fibers may cross
- Primary visual cortex: Located in the occipital lobe, responsible for initial processing
- Two processing streams:
- Dorsal stream (“where” pathway): Analyzes location, movement, and direction of objects
- Ventral stream (“what” pathway): Identifies and recognizes objects
 V. Next Steps
V. Next Steps
-
The lecture will delve deeper into the details of how light enters the eye. Turning Light into Neural Information Visual Fields