Key Ideas:
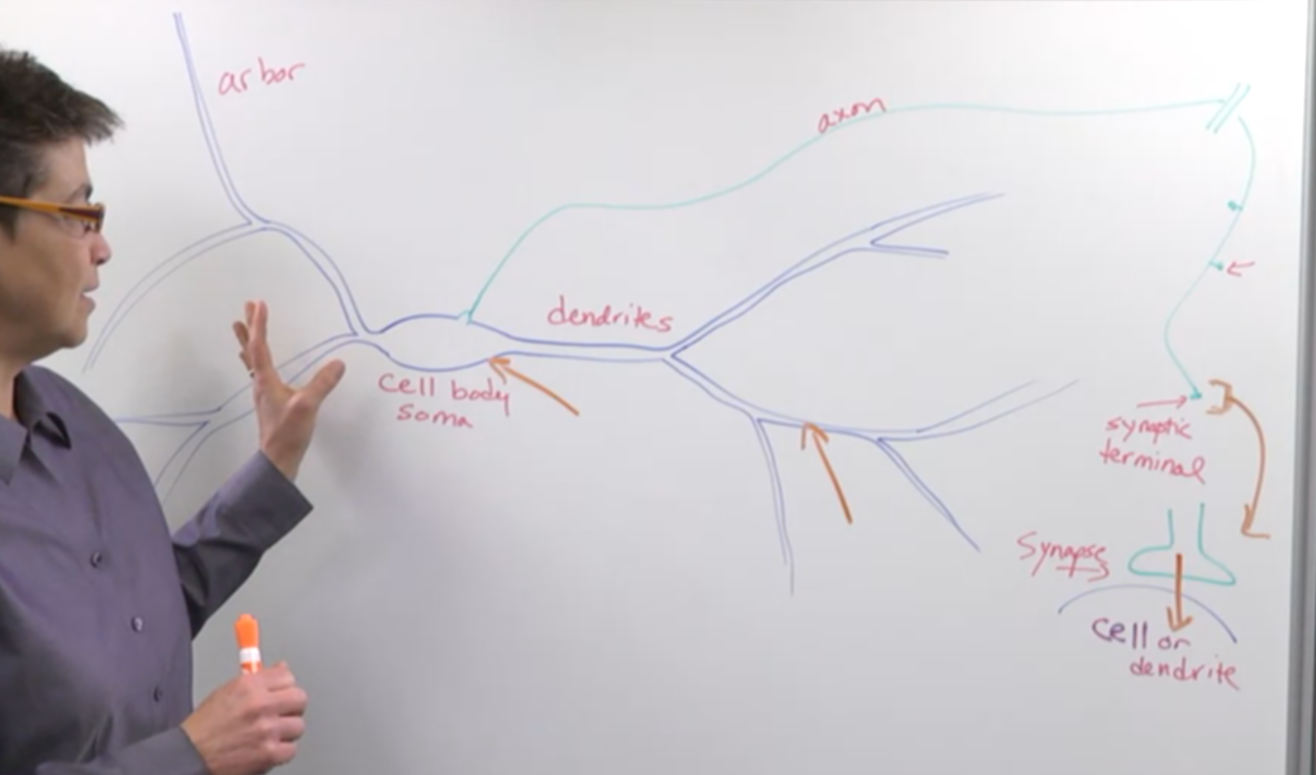
- Parts of Neurons: Neurons consist of four main parts, each with specific functions:
-
- Central part of the neuron containing the nucleus and DNA, akin to “city hall” issuing orders.
- Manufacturing plant for proteins and energy production, vital for cell function and maintenance.
-
- Branching extensions from the cell body responsible for gathering information.
- Function as the ears or sentries of the neuron, receiving incoming signals. Dendritic Arbor: Dendrites form a branching structure termed the dendritic arbor or dendritic tree, enhancing their capacity to gather information.
-
- Single long projection responsible for transmitting processed information to distant locations.
- Can extend over significant distances, up to a meter or more. Axonal Function: Axons transmit processed information over long distances, facilitating communication between neurons and other cell types.
-
- Communication centers located at the end of axons.
- Transfer information to the next cell via synapses, which are specialized junctions. Synaptic Transmission: Synaptic terminals facilitate the transfer of information to the next cell via specialized junctions called synapses.
-
Cellular Communication: Neurons communicate with various cell types, including other neurons, muscles, glands, and cardiac muscle, through synaptic transmission.
Diversity of Neurons: Neurons exhibit significant variability in their appearance and function, even within the same region of the nervous system.